27 979
Uczestników
różnego typu aktywności szkoleniowych i wykładowych
432
Wydarzeń
szkoleń / warsztatów / wykładów
558
Materiałów edukacyjnych
w formie gotowych artykułów, programów, haseł słownikowych
151
Wspartych firm
w procesie transformacji cyfrowej
Platforma Cyfrowa
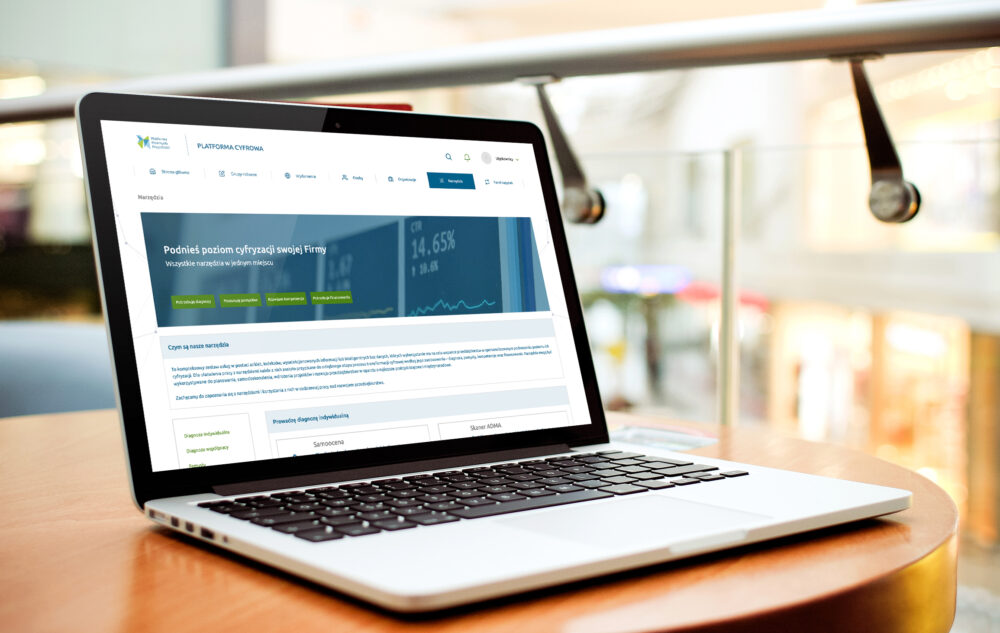
Nowa przestrzeń współpracy
Platforma Cyfrowa stanowi bezpłatną, międzybranżową przestrzeń skoncentrowaną na przekazywaniu wiedzy, wymianie doświadczeń, przedstawianiu konkretnych rozwiązań i innowacyjnych idei z zakresu nowoczesnych technologii, transformacji cyfrowej i rozwoju firm w kierunku przemysłu przyszłości.
To przestrzeń współpracy wszystkich zainteresowanych współpracą rynkową, partnerów, przedstawicieli nauki i instytucji publicznych.