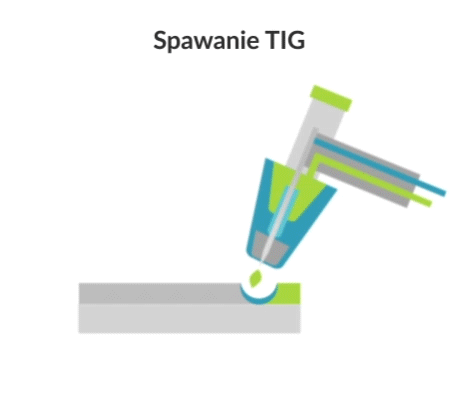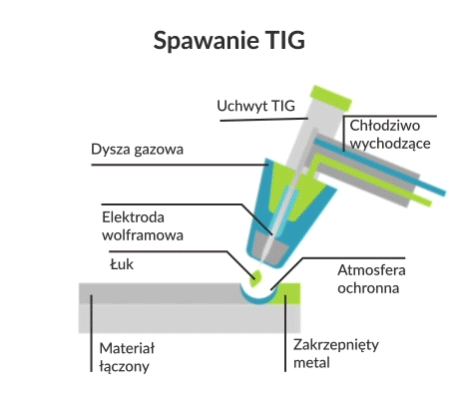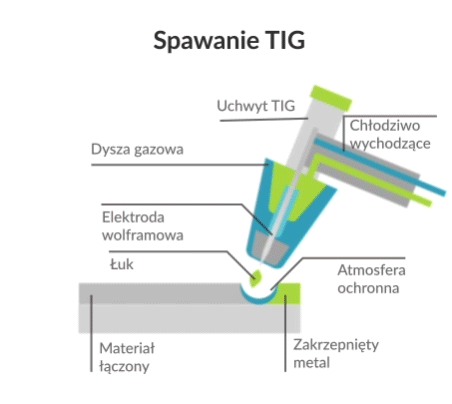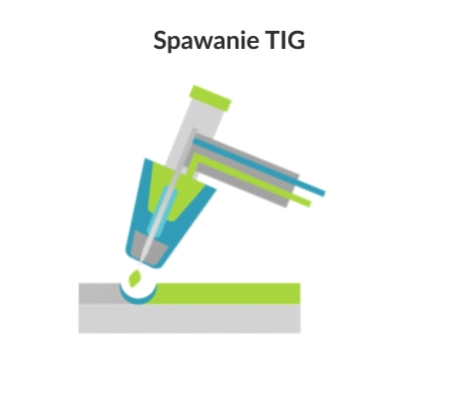
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is an arc welding process in which a weld is produced using a non-wearing tungsten electrode. Using an inert gas shield instead of slag to protect the weld pool, the process was a very attractive substitute for gas welding and manual arc welding. TIG has played a major role in making aluminium acceptable for high-quality welding and structural applications.

Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
pl.
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
joining various materials
Industry usage
power industry, aviation industry, aerospace industry
Alternative technologies
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- versatility of the method
- applicable to thin walls
- high weld quality
- possibility of automation
Disadvantages
- low welding speed
- TIG welding operations may cause interference with other equipment
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
Examples of products
- pipe welding
- welding of pipelines
- welding of thin sheets
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- welding machine
- gases
- binder
Required competences
- welding courses
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology
- Łukasiewicz Research Network – Institute of Welding
Legal conditions
- none