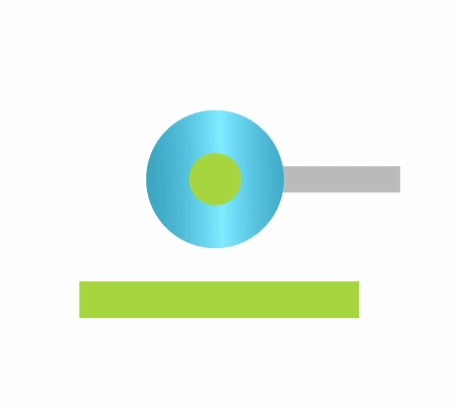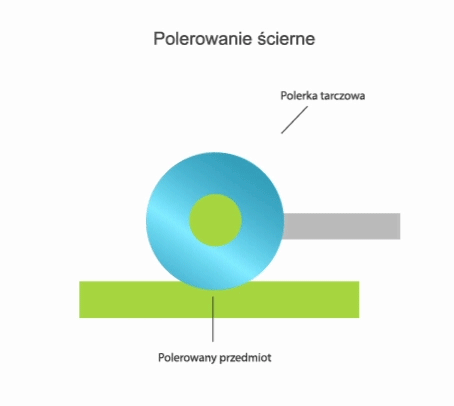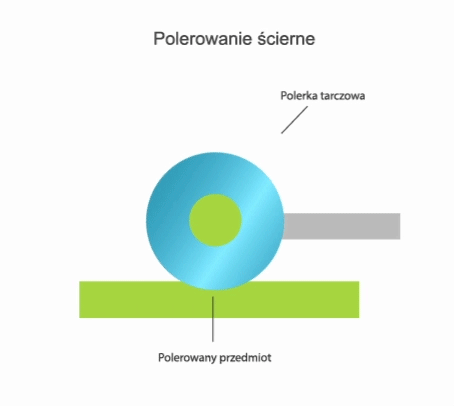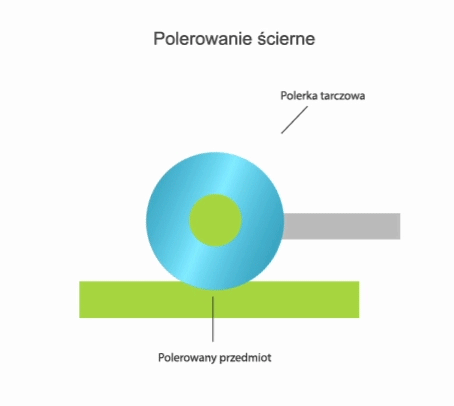
Depending on the process type, polishing can be carried out in the following ways:
- abrasive method – the function of the tool in abrasive polishing is performed by abrasive polishing pastes applied to polishing discs or belts, and the process of improving the properties of the surface layer of the workpiece takes place as a result of micromachining, friction and physico-chemical phenomena.
- chemical method – the polished workpiece is immersed in a bath containing a suitable chemical solution that acts on the surface layer.
- electrochemical method – the polished workpiece is connected in a galvanic bath to a positive electrode (anode), as a result of which the irregularities on the workpiece are covered by a layer of products with a higher resistivity than the electrolyte. The current density is greater at the peaks of the rough surface than in the recesses, followed by dissolution of the metal – i.e. a reduction in surface roughness.
- hydrodynamic (jet) polishing – workpieces are clamped in a chuck and lowered into a rotating tank filled with polishing media. During the process, the polishing media flows around the workpiece, which also rotates.
- flame polishing – the process of improving the condition of the surface layer of the workpiece occurs as a result of high temperatures generated by a gas torch.