Minimum Quantity Cooling Lubrication (MQCL) is a subtractive manufacturing process in which a small amount of machining fluid is supplied to the machining zone in the form of an aerosol. The application of machining fluid droplets is carried out using special equipment that produces oil droplets with a size range typically between 0.1 and 2 μm. MQCL machining is most commonly used for the following machining processes: MQCL turning, MQCL milling, MQCL drilling, and MQCL grinding.

Minimum Quantity Cooling Lubricating machining (MQCL)
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
subtractive manufacturing of various parts (similar to turning, milling, drilling, grinding)
Industry usage
all industries
Alternative technologies
- conventional machining
- ultrasonic machining
- laser assisted machining (LAM)
- cryogenic machining
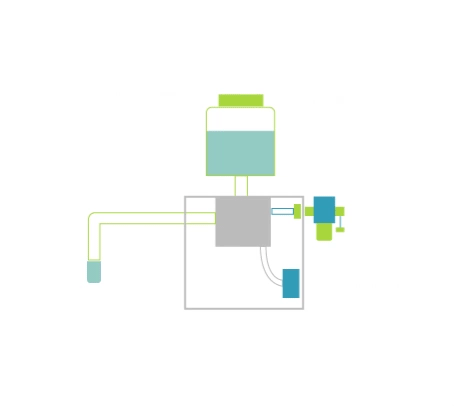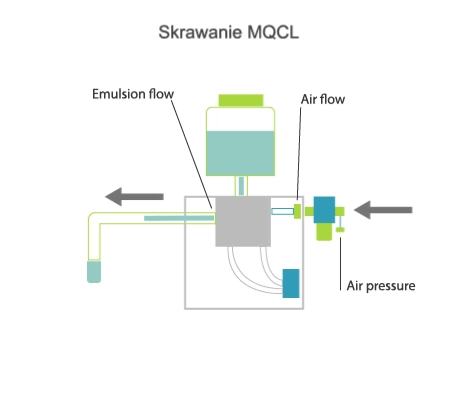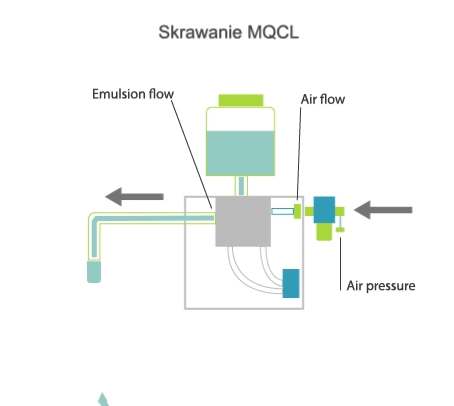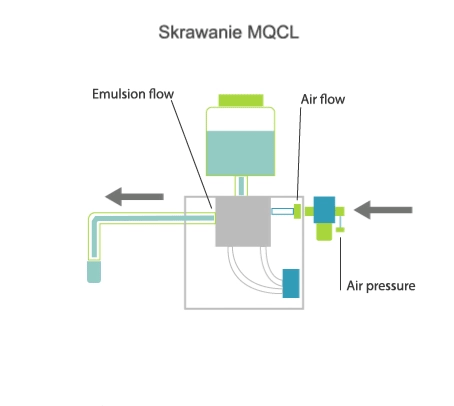
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- the ability to increase the volumetric efficiency of machining (compared to the effects of conventional machining)
- the ability to reduce the wear intensity of the cutting edge (compared to the effects of conventional machining
- the ability to reduce the values of the machined surface roughness parameters (compared to those obtained with conventional machining)
- reduced use of personally and environmentally non-inert machining fluids (compared to conventional machining with immersion cooling/lubrication of the machining zone)
- the ability to reduce machining loads (reduced energy consumption compared to conventional machining processes)
Disadvantages
- significant capital expenditure (purchase of additional oil mist generation equipment)
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
- hard materials
- hardened materials
Examples of products
- machine bodies
- cutting tools
- radiator cooling pads
- crankshafts
- turbine blades
- compressor rotors
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- machine tool
- oil mist generation equipment
- cutting tools
- tooling
- machining fluids
Required competences
- training in machining and programming of CNC machines
- extensive practical experience in machining
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- University of Zielona Góra
- Poznan University of Technology
- Opole University of Technology
- Rzeszow University of Technology