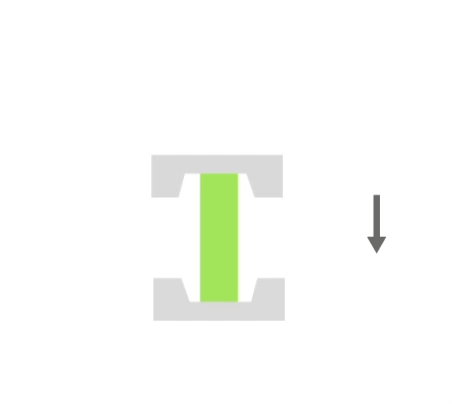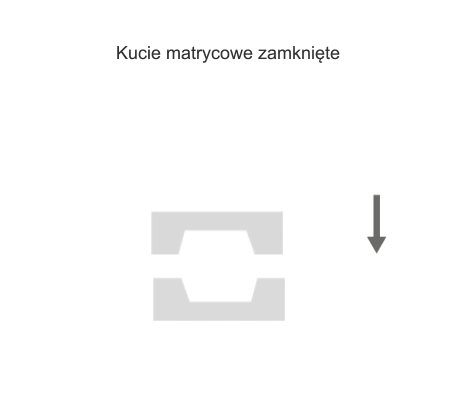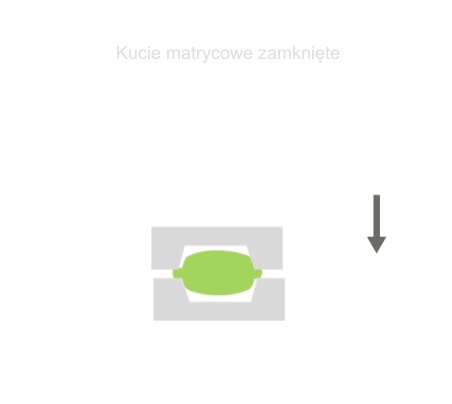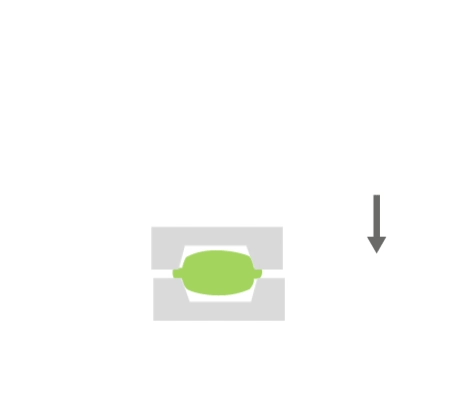
Die forging is a process in which material is placed in a mold-like die attached to an anvil. The die is then dropped onto the workpiece, causing the material to flow and fill the die. Depending on the size and complexity of the part, the tool may drop many times (many times in milliseconds) in a series of rapid movements. The excess material that is squeezed out of the die cavities is referred to as efflux. The efflux cools faster than the rest of the material and typically has higher properties than the material in the die, which helps prevent more efflux from forming. The efflux also forces the material to completely fill the die cavity, and is removed after forging.

Closed die forging
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
manufacture of forgings of complex shape and highly variable weight (from a few grams to several tons)
Industry usage
automotive, shipbuilding, defense, mining, aerospace, agriculture industries
Alternative technologies
- incremental forging
- subtractive manufacturing
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- manufacture of parts with final shape or requiring little machining
- high strength
- high dimensional tolerance
- good surface quality
Disadvantages
- high cost of tools
- dimensional limitations
Workpiece material types
- all groups of materials
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- ferrous metal alloys
- non-ferrous metal alloys
Examples of products
- construction machinery
- ball bearing components
- crankshafts
- suspension components
- electronic components
- metal watch components
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- hydraulic presses
- hammers
- swaging machine
- electric upsetting press
Required competences
- training in the use of presses
- training in the use of hammers
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Lublin University of Technology
- Czestochowa University of Technology
- Silesian University of Technology
- Wrocław University of Science and Technology
- Łukasiewicz – Poznań Institute of Technology
Legal conditions
- none