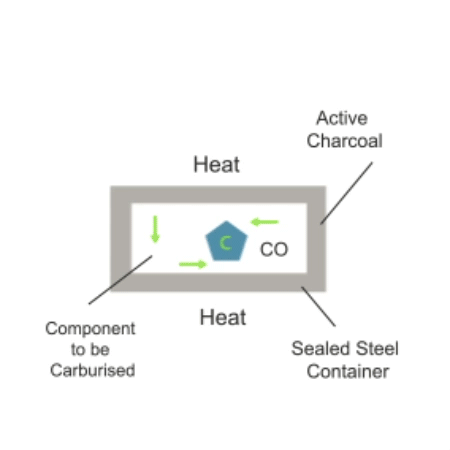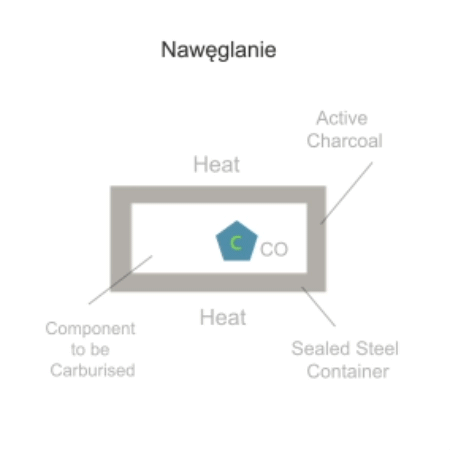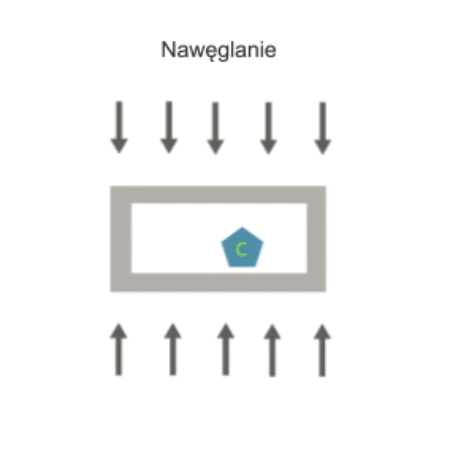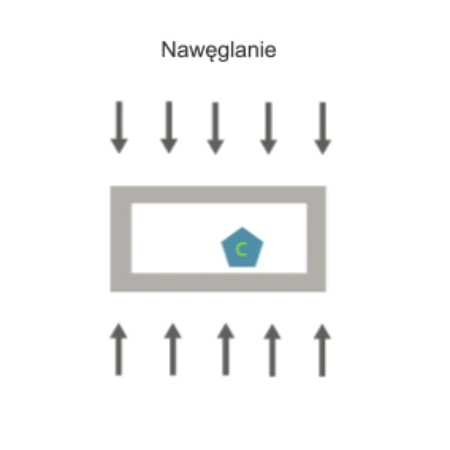
Carburising is a thermo-chemical treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon when heated in the presence of carbonaceous material.
Depending on time and temperature, the carbon content of the affected area may vary. Longer carburising times and higher temperatures tend to increase the depth of carbon diffusion. When iron or steel is rapidly cooled by quenching, the higher carbon content on the outer surface becomes hard due to the transformation of austenite to martensite, while the core remains soft and hard as a ferritic and/or perlitic microstructure.