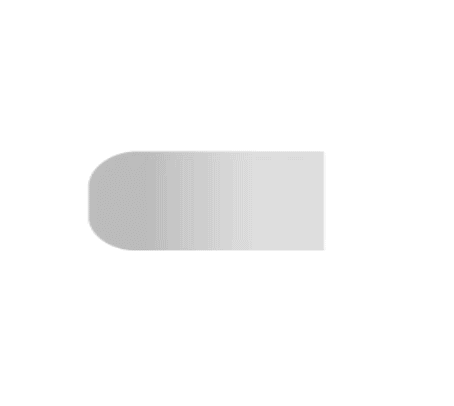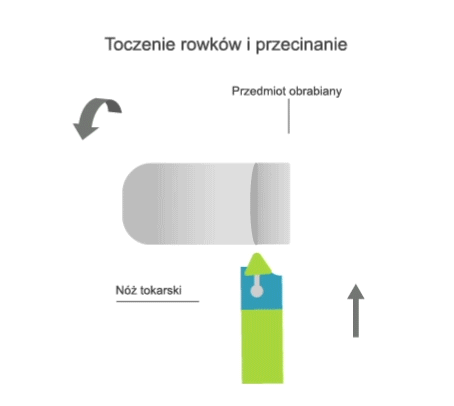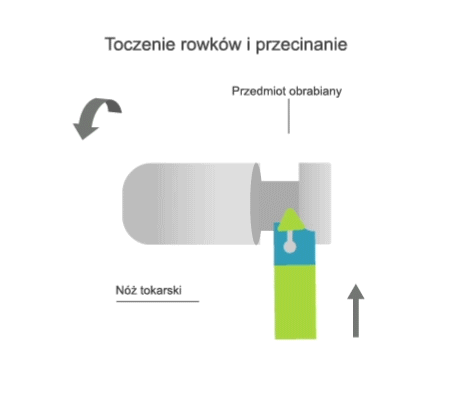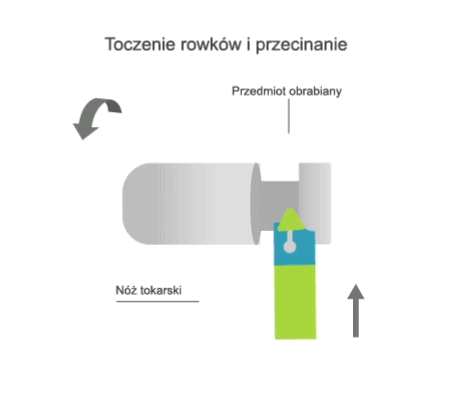
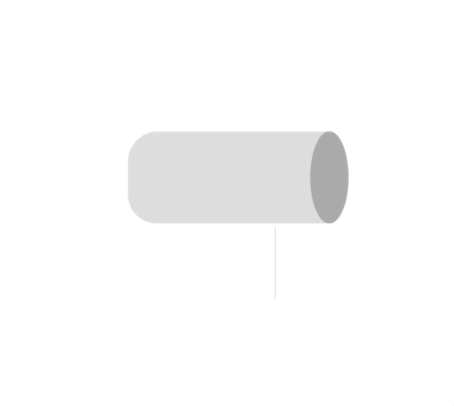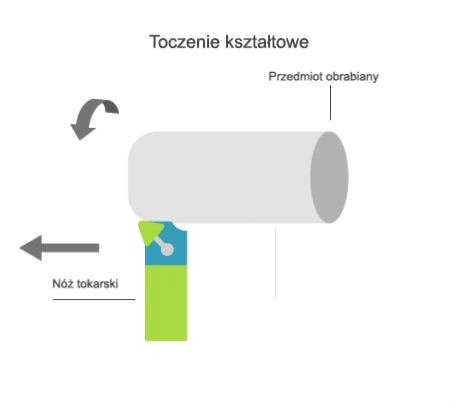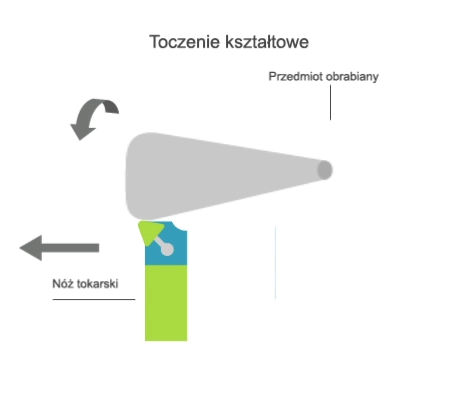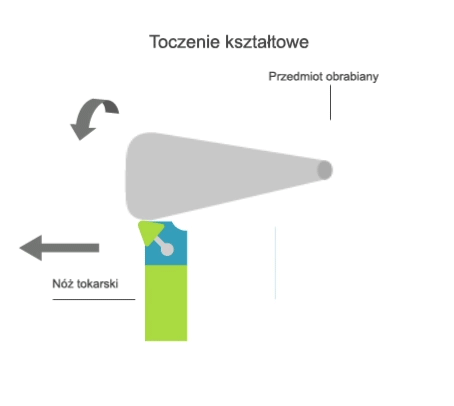
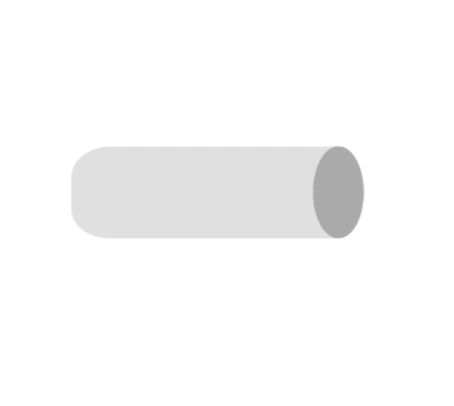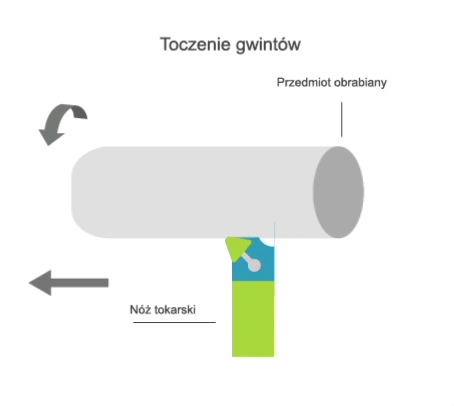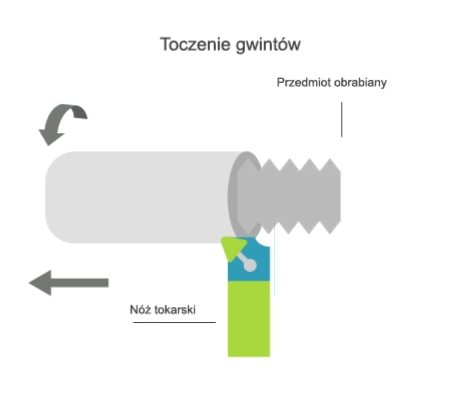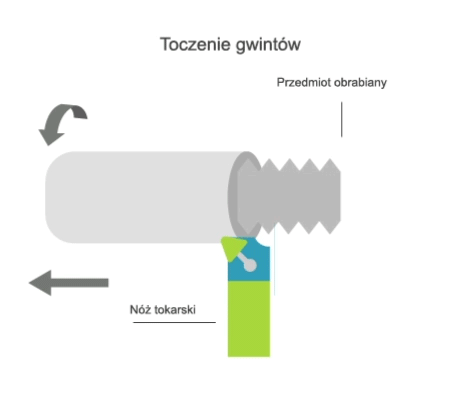
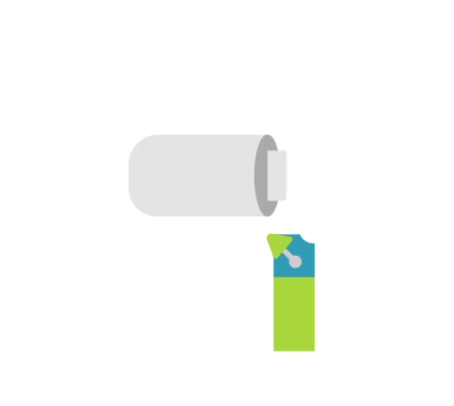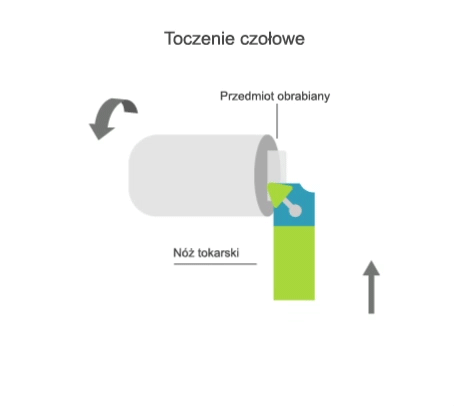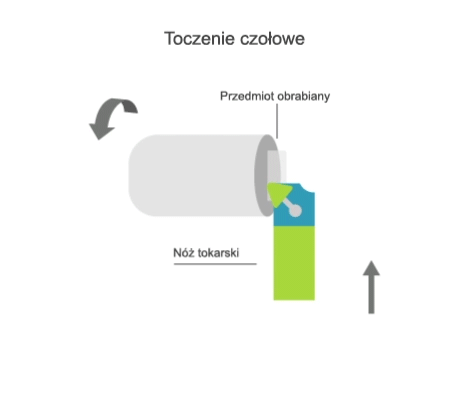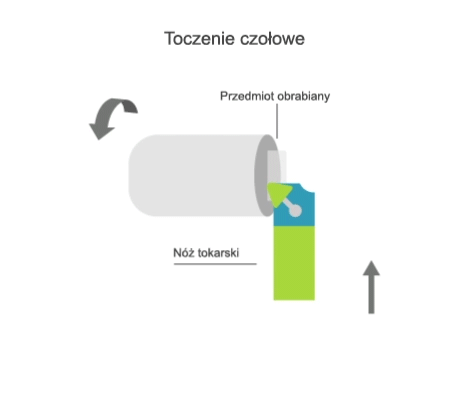
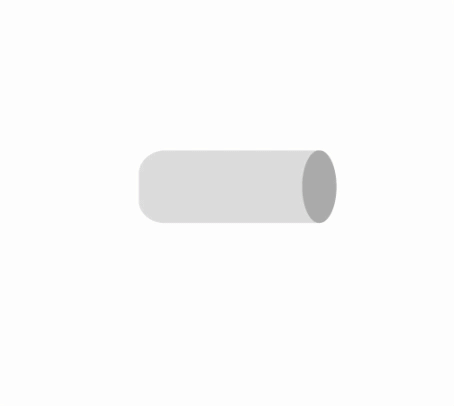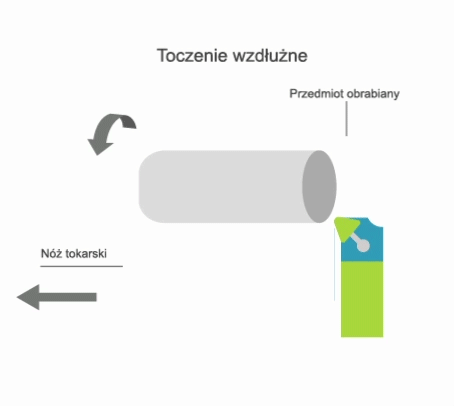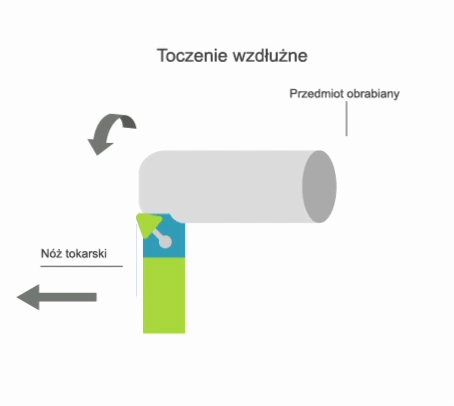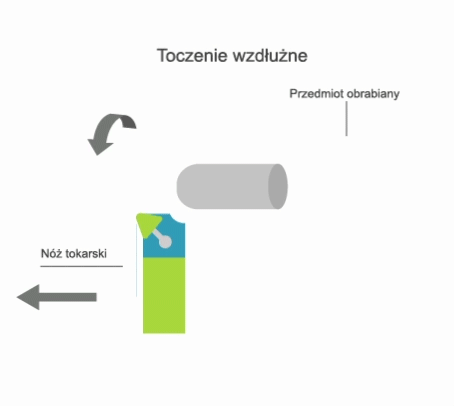
Turning is a machining process that involves the subtractive manufacturing of axisymmetric parts with the use of a turning tool. In turning, the primary (rotary) motion is performed by the workpiece, and the feed motion is performed by the cutting tool.
There are two kinematic variations of turning:
- longitudinal, where the feed motion is parallel to the axis of rotation of the part;
- transversal, where the feed motion is perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the part.