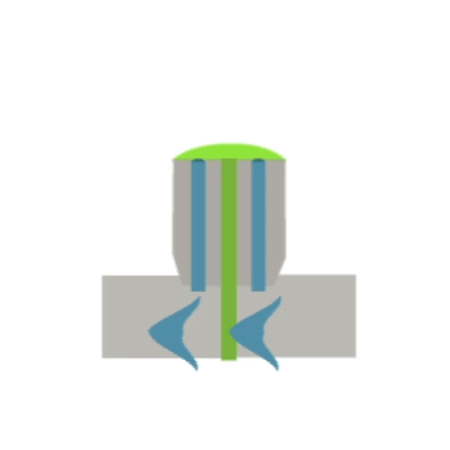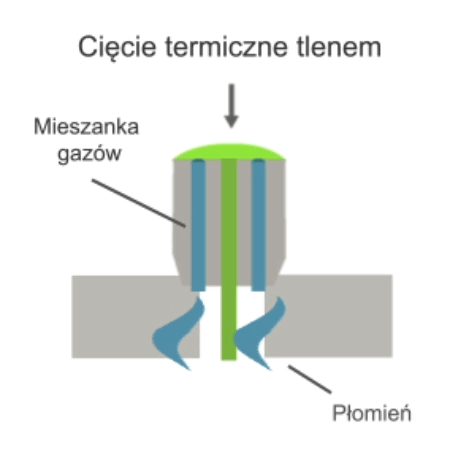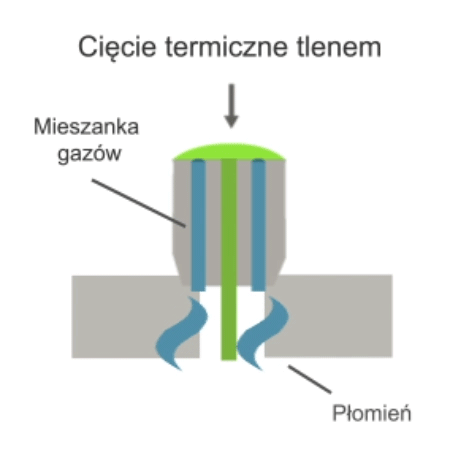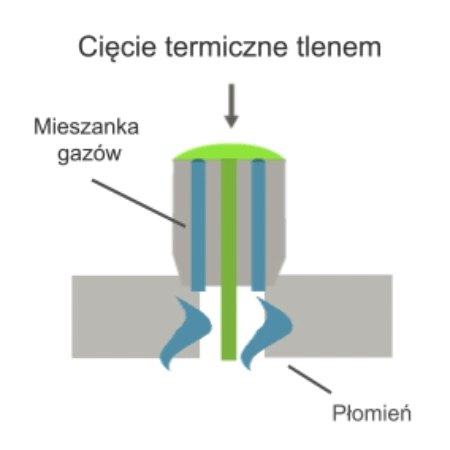
Thermal oxygen cutting involves burning a slit in the material using a jet of oxygen in conjunction with a heat source, usually an oxy-acetylene gas flame. In addition to acetylene, other flammable gases such as propane, butane, methane or hydrogen can also be used. During the process, the workpiece material is heated to combustion temperature and the molten metal is then removed from the slit using a high-pressure gas jet.
The technology makes it possible to cut thick sheet metal and sheet metal packages (up to 200-300 mm), as well as varnished or corroded parts.