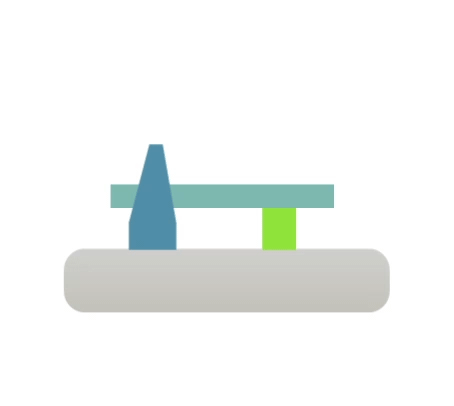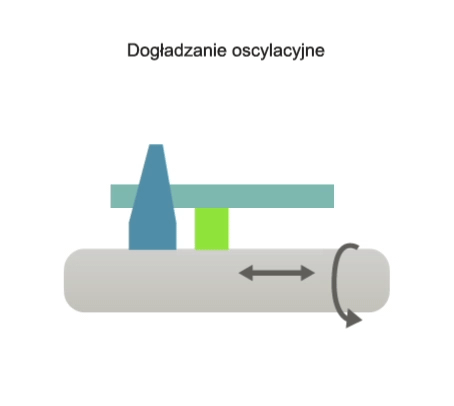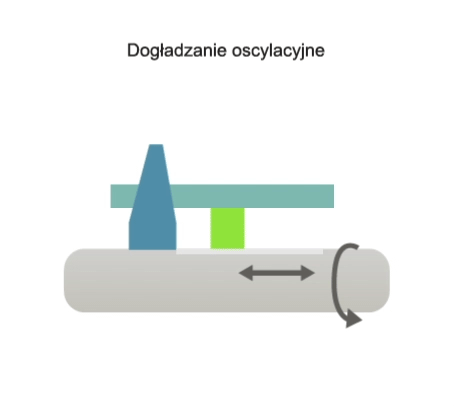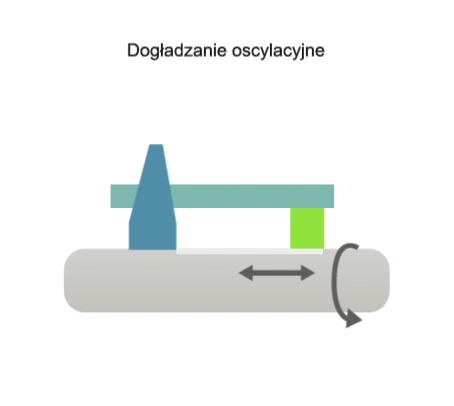
Superfinishing is a high-precision abrasive machining process in which the cutting tool, in the form of an abrasive stone or belt, performs an oscillating motion (i.e. a rectilinear motion with a low stroke rate and high stroke frequency) and may also perform a feed motion. The workpiece, on the other hand, performs a rotary motion and, in some variations of the process, a feed motion.
The main purpose of oscillating superfinishing is to remove surface micro-roughness left over from the previous finish machining process (e.g. turning, grinding, broaching).