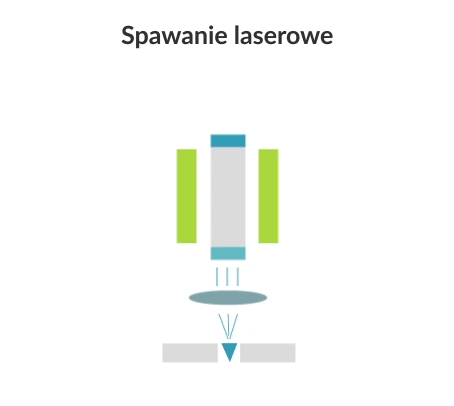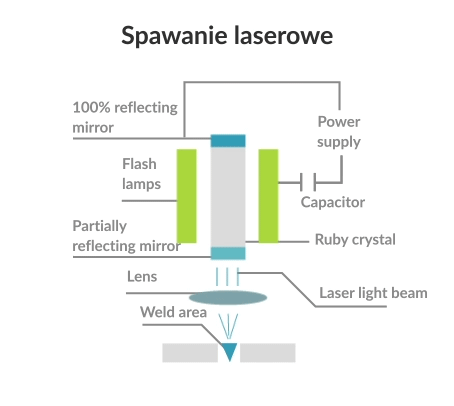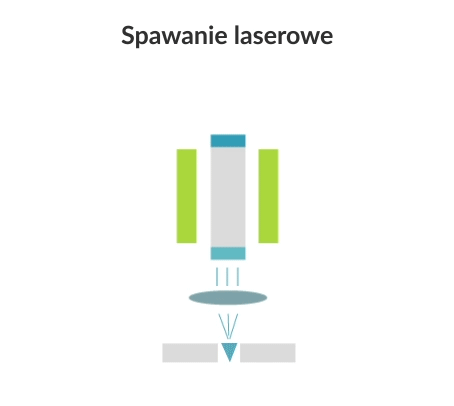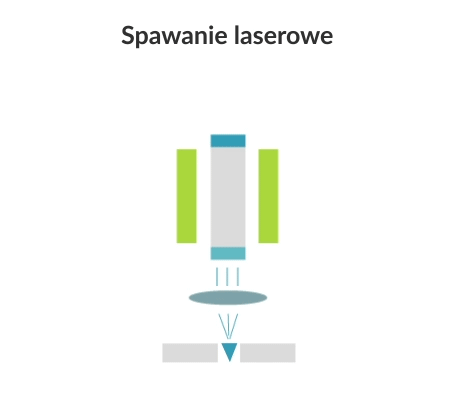
Laser beam machining is a machining method that uses the vapourisation of the workpiece material by means of a beam of laser radiation (photons) emitted by a technological laser. The very short machining time and the large amount of energy delivered to the machining site allow the process to be carried out without combustion, minimising chemical pollution and eliminating oxidation.
In addition to subtractive manufacturing, laser beam machining can also be used for welding and spraying.
In laser welding, the contact area of the parts to be joined is molten by the heat generated by applying a concentrated beam of high-powered photons to the area.
In laser overlaying welding, the energy of the photon beam melts the additional material in the form of powder or wire in a gas shield and simultaneously melts the substrate metal, which, when fused together, forms the build-up weld.