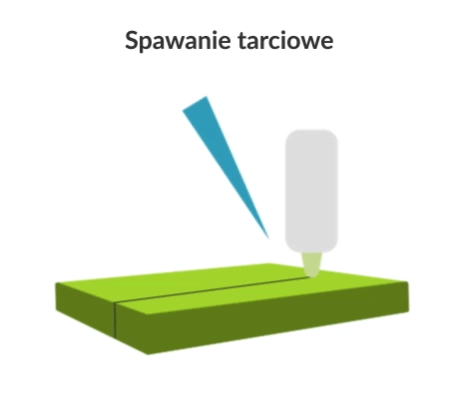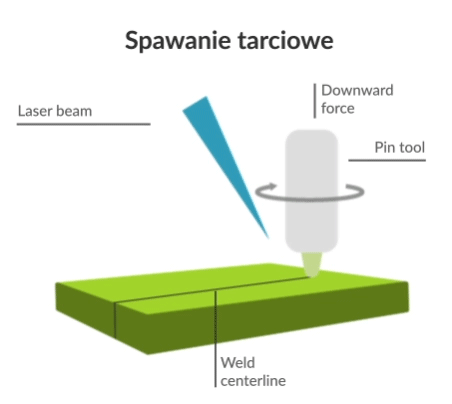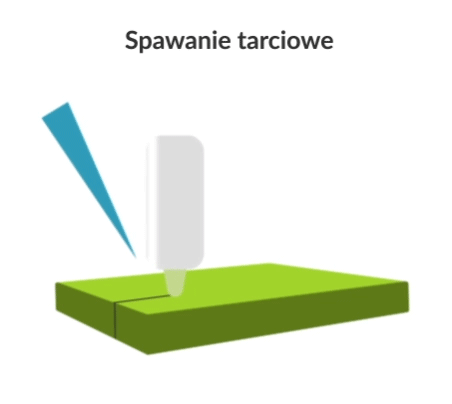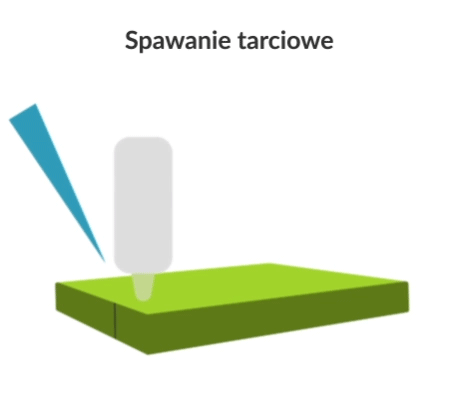
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is an advanced technique for continuously joining materials. In FSW, a cylindrical, conical tool with a profiled probe is rotated and slowly inserted into the joint line between the two pieces of sheet or plate to be joined. The parts are clamped to prevent the contacting surfaces from separating during the welding process. Friction heat is generated between the wear-resistant welding tool and the materials being joined. The heat softens or melts the material and allows the tool to move along the joint line. The plasticised material is transferred from the leading edge to the trailing edge of the tool probe and forged by close contact with the tool arm to create a weld between the two components.

Friction stir welding (FSW)
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
unit
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
joining various materials
Industry usage
shipbuilding and offshore industries, aviation industry, automotive industry, rail transport, robotics
Alternative technologies
- other welding methods
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- increased productivity especially with thicker materials
- possibility of continuous welding
- possibility of welding almost all thermoplastics
- simple joint design
- almost no weld flash
- automated process
Disadvantages
- joining of flat surfaces only
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
Examples of products
- turbine shafts
- cutting tools
- drill pipes
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- friction stir welding machine
Required competences
- high operator qualification
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Łukasiewicz – Górnośląski Instytut Technologiczny (GIT)
- Military University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none