Cryogenic machining is a subtractive manufacturing process in which the machining zone is cooled by a medium with a temperature below -150゚C. The coolant used in cryogenic machining is usually liquid nitrogen (LN2). Cryogenic machining is mainly used for the following machining processes: turning, milling, drilling.

Cryogenic machining
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch, unit
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
effective and efficient machining (e.g. turning, drilling, milling) of difficult-to-machine materials (mainly titanium and nickel alloys)
Industry usage
all industries, mainly automotive industry, aviation industry, biomedical industry
Alternative technologies
- conventional machining
- LAM machining
- MQCL machining
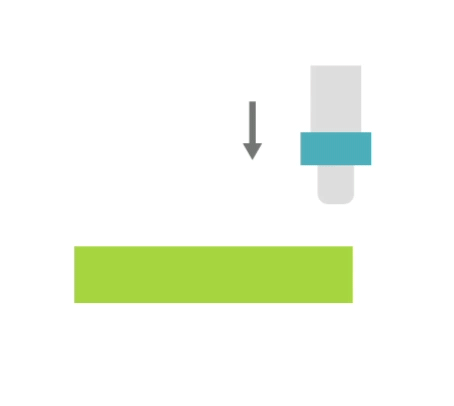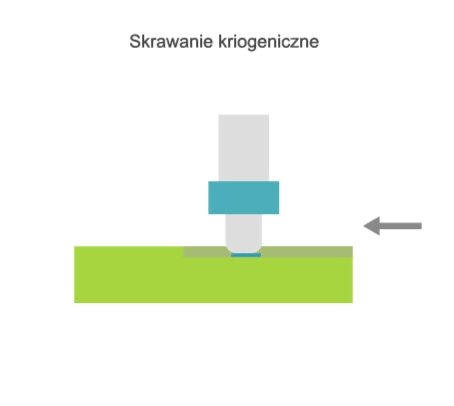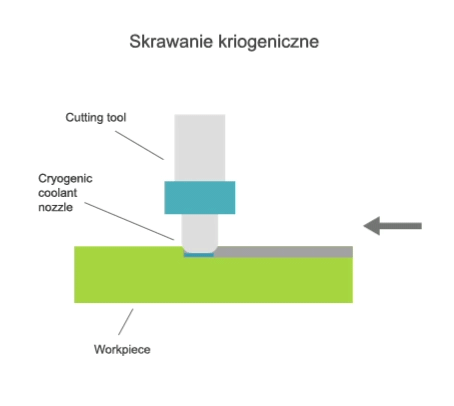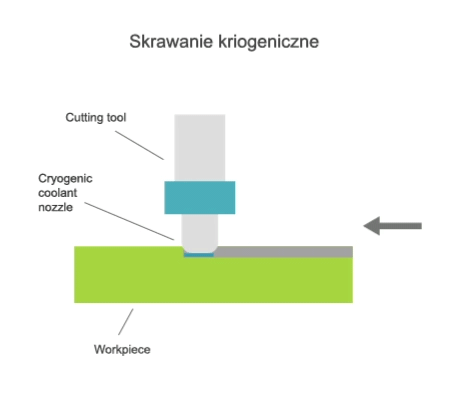
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- ability to reduce the cutting temperature of difficult-to-machine materials (compared to conventional machining)
- ability to reduce wear intensity and increase blade life when machining difficult-to-machine materials (compared to conventional machining)
- possibility of reducing surface roughness values of machined materials (compared to conventional machining)
- elimination of environmentally and personally harmful conventional machining fluids from the machining process
- environmental inertness of the coolant
Disadvantages
- significant personnel qualification requirements (experience in machining)
- significant capital expenditure (for the purchase of liquid nitrogen and supply to the machining zone/ modification of machine tool design)
Workpiece material types
- mainly titanium alloys
- heat-resistant nickel alloys
- heat-resistant cobalt alloys
Examples of products
- turbine aircraft blades
- surgical instruments
- cutters
- drills
- lathes
- rollers for mills
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- turning/milling centre
- cutting tools
- tooling
Required competences
- training in machining and programming of CNC machines
- extensive practical experience in machining
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- Poznan University of Technology
- Opole University of Technology