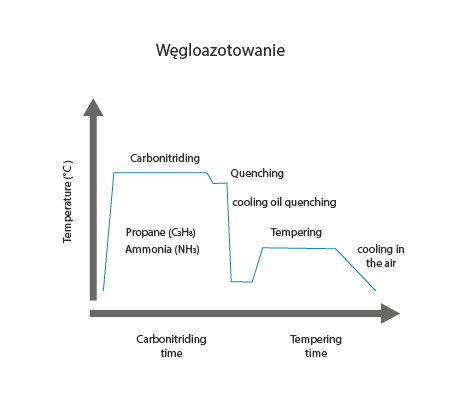
Carbonitriding (nitrocarburising) is one of the thermo-chemical processes for steel, in which the surface of steel objects is simultaneously saturated with carbon and nitrogen at temperatures ranging from 500 to 950°C. The application of heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering produces a hard and wear-resistant surface layer. Depending on the nature of the substance releasing the carbon and nitrogen, the carbonitriding process can be carried out in bath or gaseous form.

Carbonitriding
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
change of the properties of materials through thermal and chemical processes
Industry usage
automotive, mechanical, tooling industries
Alternative technologies
- nitriding
- carburising
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- increased hardness of steel
Disadvantages
- high costs
Workpiece material types
- steel
Examples of products
- gears
- shafts
- pistons
- rollers
- bearings
- levers in hydraulic/pneumatic/mechanical systems
- dies for forging
- dies for stamping
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- furnaces
- vacuum furnaces
Required competences
- knowledge of materials science
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none