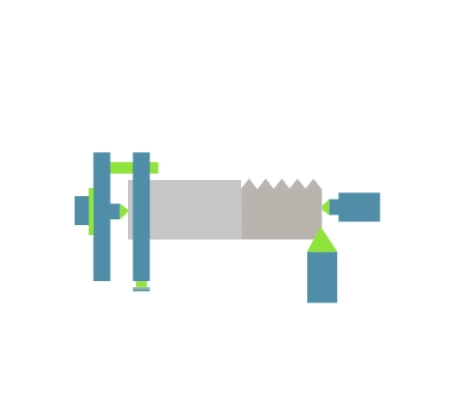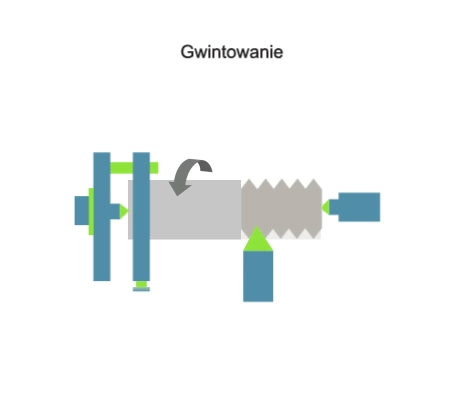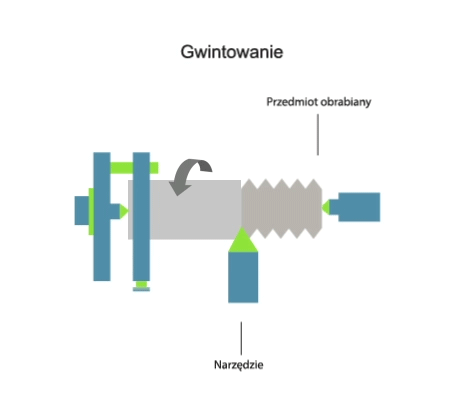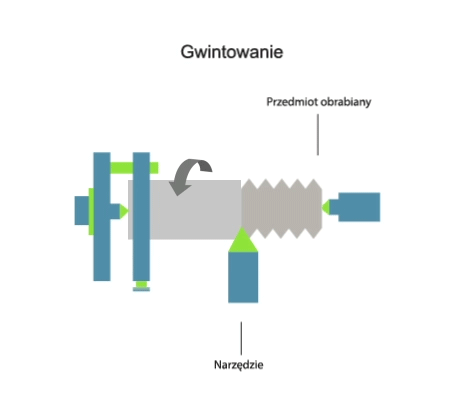
Threading (also: tapping) is a machining process involving the subtractive manufacturing of external or internal threads. The tapping process (depending on the type of machine tool used) can be carried out using: taps, thread turning tools, die heads, thread milling cutters or threading dies. The thread machining process can be carried out on: lathes, milling machines, threading machines or by hand. Threads can also be produced by plastic forming technique – rolling.

Threading/tapping
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch, unit
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
subtractive manufacturing of internal and external threads
Use in industry
all industries
Alternative technologies
- thread forming
- rolling
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- a basic and versatile technique for the subtractive manufacturing of external and internal threads
Disadvantages
- use of machining fluids that are not inert to people and the environment
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
- hard materials
- hardened materials
Examples of products
- threaded rods
- gun barrels
- threaded holes that allow the use of screws
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- drilling machine
- lathe
- milling or threading machine
- cutting tools
- tooling
- machining fluids (optional)
Required competences
- training in machining
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
Legal conditions
- none