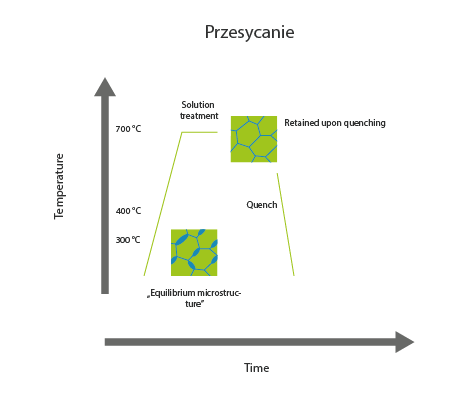
Solution heat treatment is a heat treatment process designed to consolidate austenite, mainly in steels, to increase corrosion resistance. Solution heat treatment is widely used for austenitic steels. It is also used to refine high-alloy high-strength steels and steels with special magnetic properties. The solution heat treatment improves plasticity at the expense of HV and strength.
The general process involves heating the steel to the temperature at which the austenitic transformation takes place, followed by rapid cooling, similar to quenching.
The main difference between quenching and solution heat treatment is that solution heat treatment avoids the formation of martensite. Therefore, solution heat treatment can only be applied to steels where the martensite start temperature is lower than the ambient temperature. This is particularly true of high-carbon steels and those containing alloying additions that lower this temperature and stabilise the austenite, such as nickel.