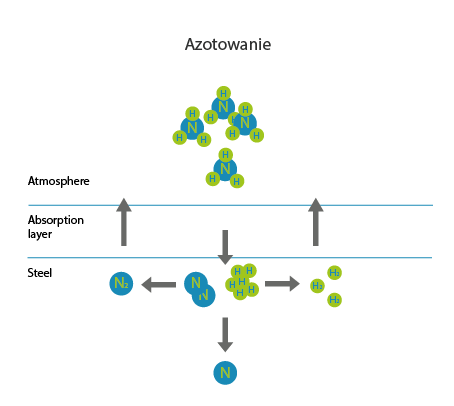
Nitriding is a thermochemical treatment process in which nitrogen is diffused into the surface of a metal to create a hardened surface. These processes are most commonly used on low-alloy steel. They are also used on titanium, aluminium and molybdenum.

Nitriding
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
increase in surface hardness, increase in abrasion resistance
Use in industry
aviation industry, defence industry
Alternative technologies
- carburising
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- increased hardness
- increased fatigue strength and abrasion resistance
- relatively low cost
- improved corrosion resistance
Disadvantages
- only for ferromagnetic materials
- depending on the alloying element content
- low controllability of nitrogen penetration thicknesses into the material
- can result in increased roughness
Workpiece material types
- low-alloy steel
- alloy steel
- titanium
- aluminium
- molybdenum
Examples of products
- engine components
- structural components
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- nitriding furnaces
Required competences
- training in furnace operation
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none