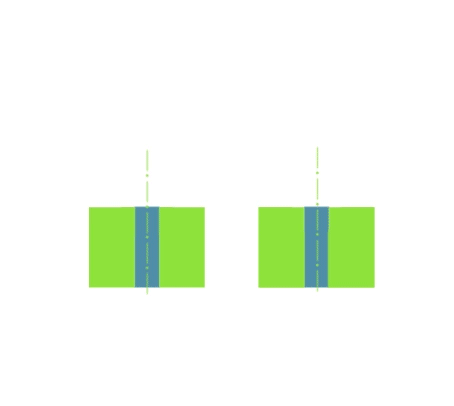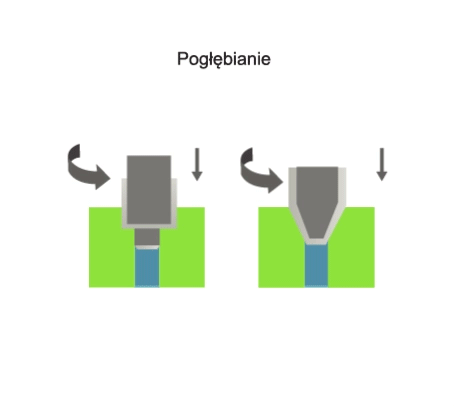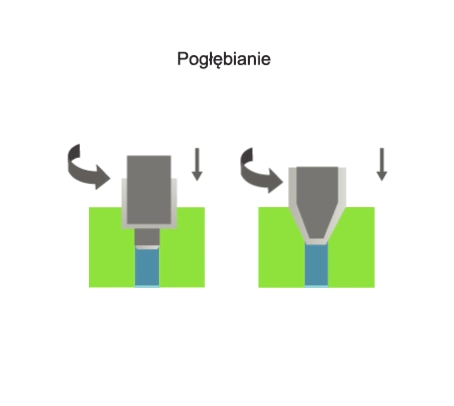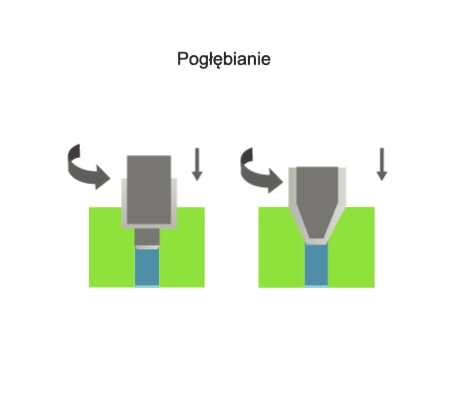
Counterboring is a method of machining that involves changing the shape and dimensions of a part of a hole or
the face associated with that hole. The counterboring process is carried out using multi-blade tools called counterbores. During counterboring, the primary (rotary) motion is performed by the tool. The feed motion is performed by the tool or the workpiece in a direction parallel to the counterbore axis.

Counterboring
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch, unit
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
changing the shape and dimensions of holes
Use in industry
all industries
Alternative technologies
- boring
- hole milling
- laser beam machining
- electron beam machining
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- a relatively quick technique to change the shape of the hole
Disadvantages
- use of machining fluids that are not inert to people and the environment
- significant tooling and fixture costs
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
- hard materials
- hardened materials
Examples of products
- engine shaft bushings
- precision hydraulic components
- ball bearings
- surgical instruments
- aerospace components (such as rotors and turbines)
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- drilling machine or milling machine
- cutting tools
- tooling
- machining fluids (optional)
Required competences
- training in machining