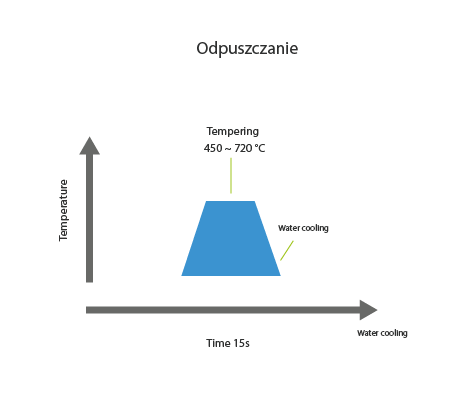
Tempering is a type of heat treatment used to increase the strength of metals, most commonly iron-based alloys. The process is performed on materials after quenching.
The metal to be machined is heated below the critical point temperature and then cooled in the air. The tempering temperature depends on the use of the material and the desired effect. There are three main groups:
- low-temperature tempering (160-300 ℃),
- medium-temperature tempering (300-500 ℃),
- high-temperature tempering (500 ℃ to Ac1).