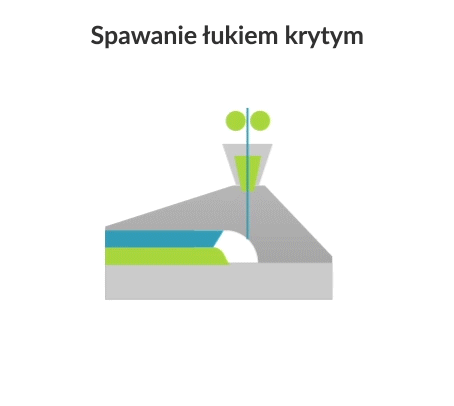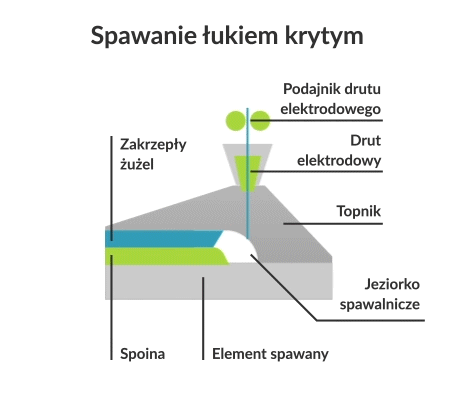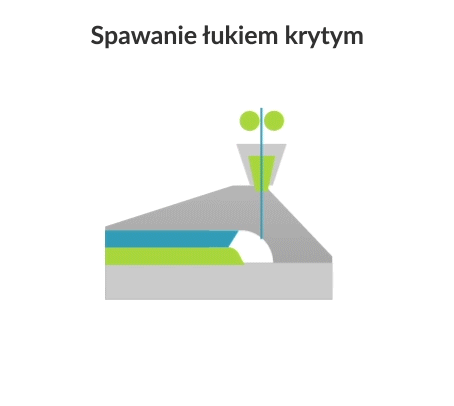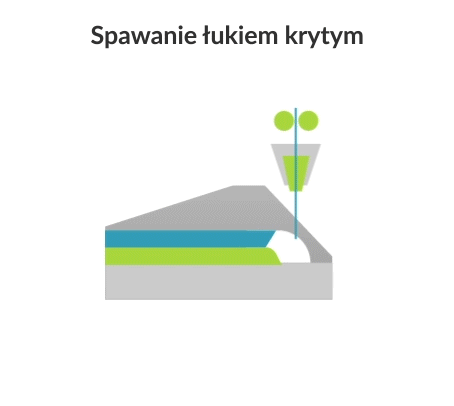
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a joining process in which an electric arc is created between a continuously fed electrode and the workpiece to be welded. The powdered flux surrounds and coats the arc and, once molten, provides electrical conductivity between the metal being joined and the electrode. It also produces a protective gas shield and slag to protect the weld area.

Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
joining various materials
Industry usage
aviation industry, marine industry, energy industry, electronics
Alternative technologies
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- high process efficiency
- high-quality welds
- high welding speed
- smooth weld surface
Disadvantages
- necessity of additional operation (flux drying)
- high cost of the welding machine
- no possibility of observing the welding process
Workpiece material types
- carbon steels
- alloy steels
- nickel alloys
Examples of products
- large steel structures
- pressure tanks
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- expensive welding equipment
Required competences
- welding certificates
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none