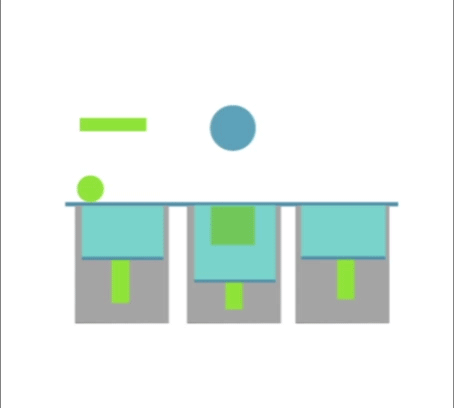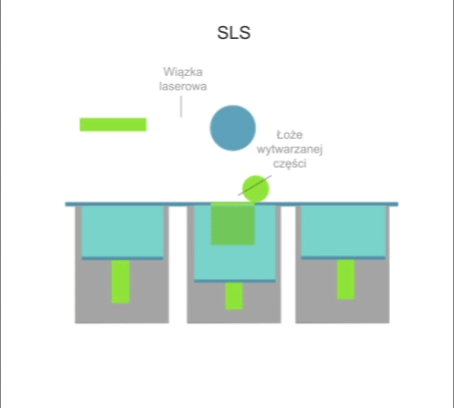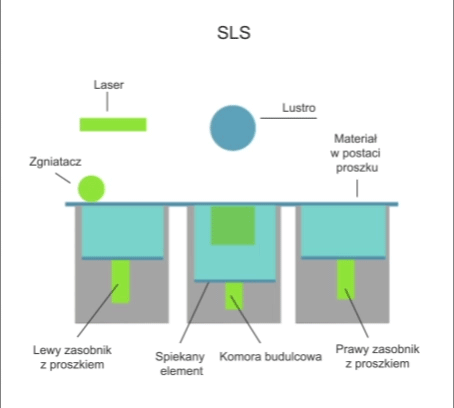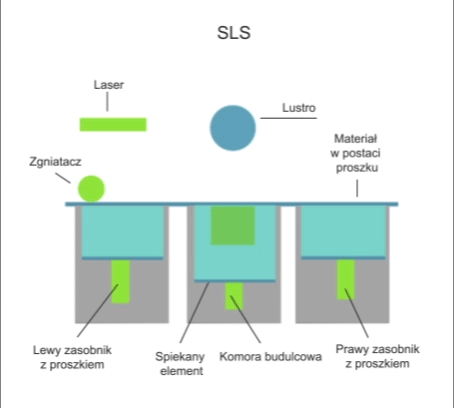
Selective laser sintering is a technique for the additive manufacturing of finished parts/products of any shape that are joined by a laser. A layer of powdered metal is placed on the machine’s work table and selectively sintered in an area defined by the shape of this layer using a concentrated photon beam generated by a laser. Depending on the design of the machine, movement in the Z (vertical) axis is performed by the work table or the head. When the work is complete, the item is extracted from the unsintered powder. Unlike the selective melting of SLM materials, the SLS process does not completely melt the powder materials.

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch, unit
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
additive manufacturing of finished parts/products of any shape
Use in industry
machine, automotive, aviation, medical, construction industries
Alternative technologies
- sintering
- casting
- machining
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- ability to produce parts with very complex shapes (impossible to achieve with machining)
- high mechanical properties of the products
- possibility to print several elements in one process (depending on dimensions)
- high geometric repeatability of manufactured parts
Disadvantages
- relatively high roughness of machined surfaces and higher porosity (compared to parts produced by conventional methods)
- the technique is not suitable for batch production/mass production
- high investment cost
- the need to control the machine’s operating environment (air purifiers and humidity/temperature control)
- printing of individual components/parts is not cost-effective
Workpiece material types
- metals
- metal carbides
Examples of products
- prototypes and small batch production of automotive components (engine housings/bumpers/interior components)
- rapid prototypes of various parts used in industry (e.g. housings or machine components)
- prototypes of surgical implants/prostheses/components used in the medical field
- prototypes of personalized and ergonomic sports shoes
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- SLS printer equipped with technological laser
- metal powders
- operating gases
Required competences
- training in metal sintering
- training in CAD/CAM systems
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- West Pomeranian University of Technology
- AGH University of Krakow
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Poznan University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology