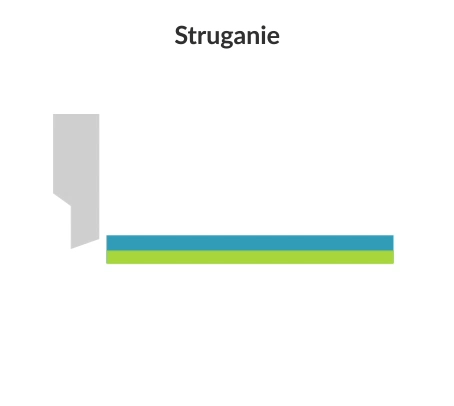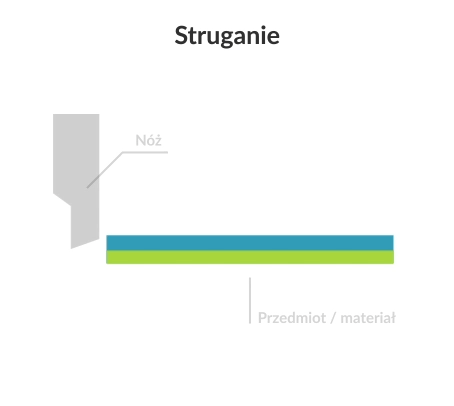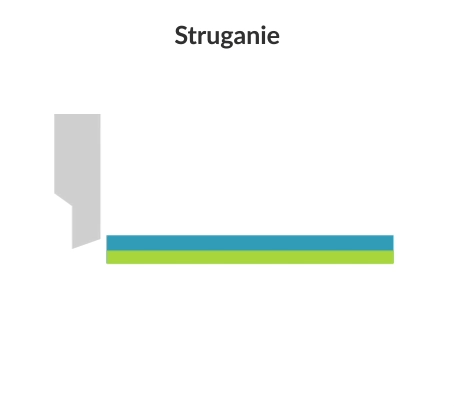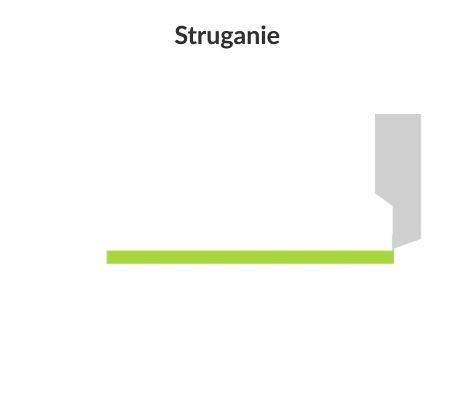
Planing (shaping) is a machining process that involves the subtractive manufacturing of flat and curved workpieces using a cutting tool (slotting tool). In the planing and shaping process, there is a rectilinear motion in the horizontal plane and an intermittent (stepped) feed motion.
Depending on the distribution of the working motions between the workpiece and the tool, a distinction is made between:
- transverse planing – the primary motion is made by the tool, and the feed motion is made by the workpiece;
- longitudinal planing – the primary motion is made by the workpiece and the feed motion is made by the tool.
The planing and shaping process is also used in the subtractive manufacturing of gears using the Sunderland method, where a planer is used to cut the teeth in the shape of a gear.