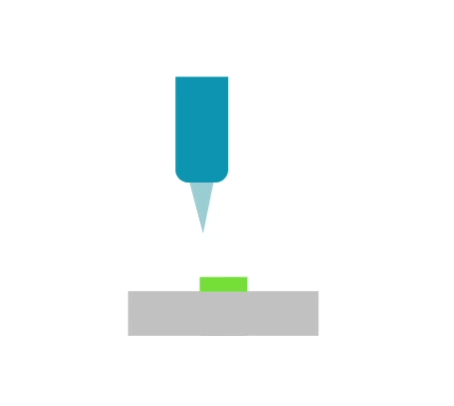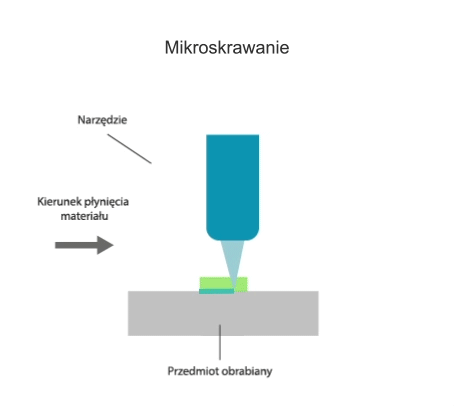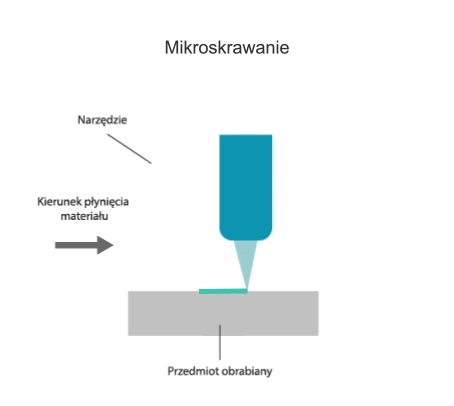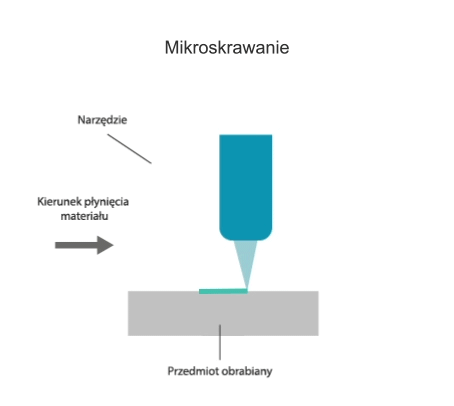
Micromachining is a subtractive manufacturing process for forming very small (miniature) parts between 1 μm and 999 μm with very high dimensional and geometrical accuracy and very low surface roughness. Micromachining processes use rotating tools (e.g. drills, milling cutters) with diameters of less than 1 mm or miniature turning tools. Micromachining is usually performed on high-precision machine tools with very high axis positioning accuracy and rigidity and capable of very high spindle speeds (typically over 50,000 rpm). Micromachining is most commonly used for the following machining processes: milling, turning, drilling

Micromachining
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
precision subtractive manufacturing of miniature components with varying geometries
Use in industry
aviation, electronic, biomedical, automotive industry, optical and precision mechanics industries
Alternative technologies
- conventional machining
- electron beam machining
- electrical discharge machining (EDM)
- electrochemical machining (ECM)
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- the ability to achieve very high dimensional and geometrical accuracy (compared to the effects of conventional machining)
- the ability to achieve very low surface roughness (compared to the effects of conventional machining)
- the ability to reduce machining loads (compared to the effects of conventional machining)
- the ability to reduce energy consumption (compared to conventional machining)
Disadvantages
- significant personnel qualification requirements (experience in machining and CNC machine programming)
- high capital expenditure (to purchase an ultra-precision machine tool with additional tooling)
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
- hard materials
- hardened materials
Examples of products
- cogs
- springs
- gears
- microneedles
- microforms and dies
- microlenses
- microprisms
- micro bevels
- micro drills
- micro milling machines
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- ultra-precision machine tool
- cutting tools
- tooling
- machining fluids (optional)
Required competences
- training in machining and programming of CNC machines
- extensive practical experience in machining
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- University of Zielona Góra
- Poznan University of Technology
- Opole University of Technology
- Rzeszow University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none