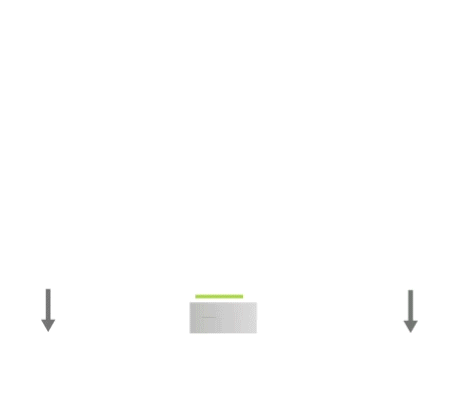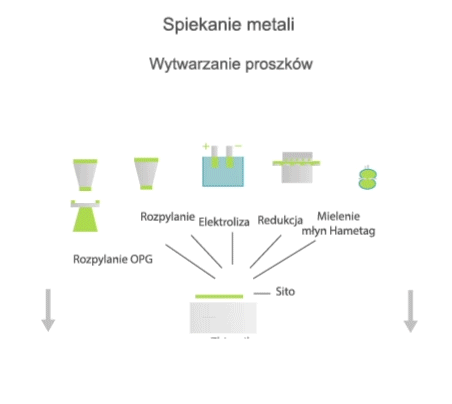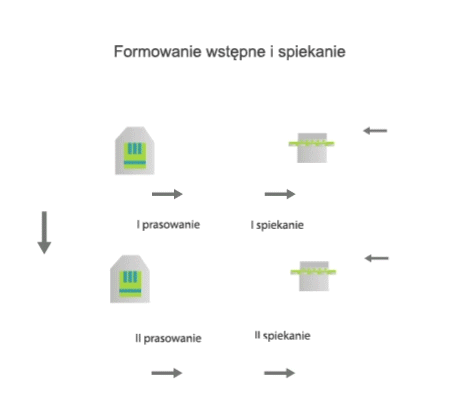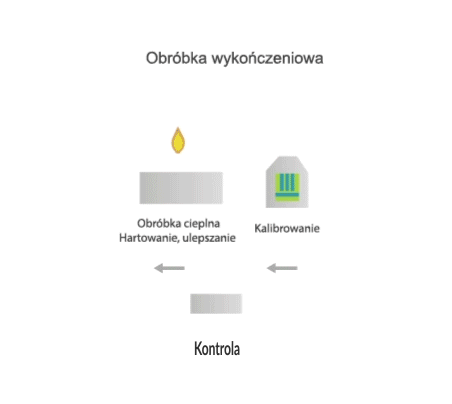
Sintering is the process by which compressed powder grains are transformed into a porous solid with specific mechanical properties. According to the Polish standard EN ISO 3252, sintering is the heat treatment of a powder or fitting at a temperature below the melting point of the main component in order to increase its strength by metallurgical fusion of the particles.
The sintering process involves annealing the molding, in a protective or controlled atmosphere, at a suitably high temperature. When sintering single-component moldings, a temperature of 70÷80% of the melting point of the metal in question is used.
When parts are made from multi-component powder mixtures, a sintering temperature higher than the melting temperature of one or more components of the mixture is used. This causes melting, and the sintering process continues with the liquid phase.
One of the latest trends in the sintering process is the SPS (Spark Plasma Sintering) technique, which uses periodically repeated pulses of direct current, lasting from a few to several hundred milliseconds, and with an intensity of up to several thousand amperes, for heating.