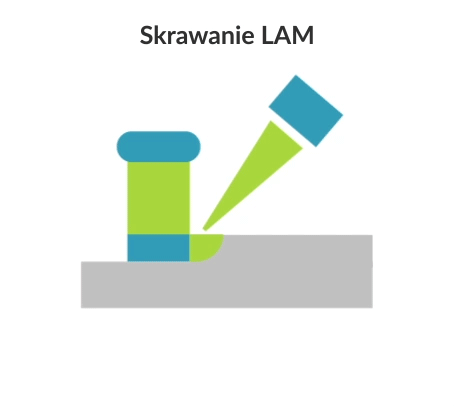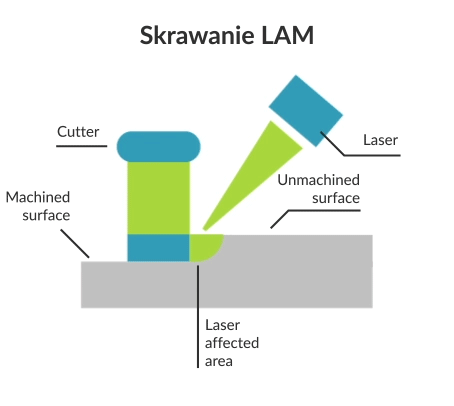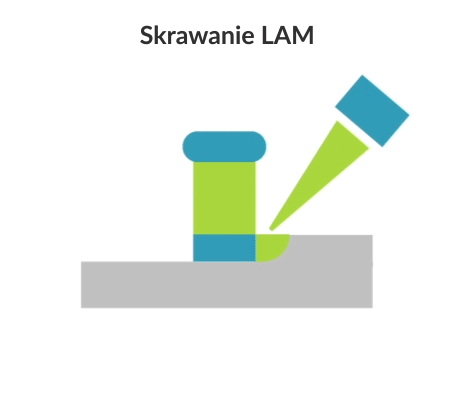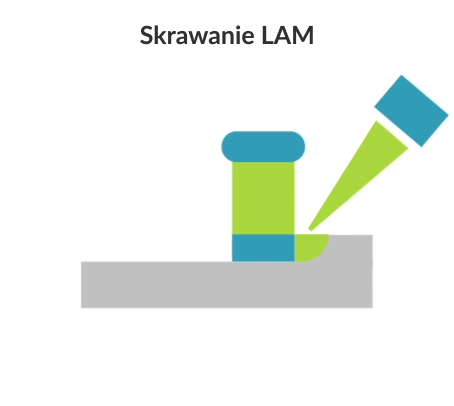
Laser assisted machining (LAM) is a subtractive manufacturing process for hard and brittle materials that uses laser beam for local heating of the workpiece material before before removing it with a conventional cutting tool (such as a turning tool or milling cutter). Laser heating of the workpiece is performed with a high-powered technological laser (e.g. CO2 laser, Nd: YAG laser).
At higher temperatures, the yield strength of the brittle workpiece material drops below the fracture toughness, allowing the machined layer to be transformed into a chip, in the sense of ductile rather than brittle fracture. Laser assisted machining is mainly used for turning and milling.