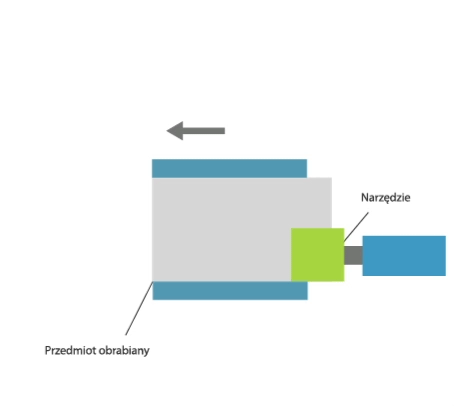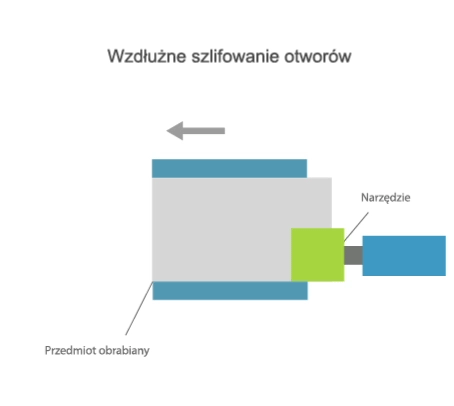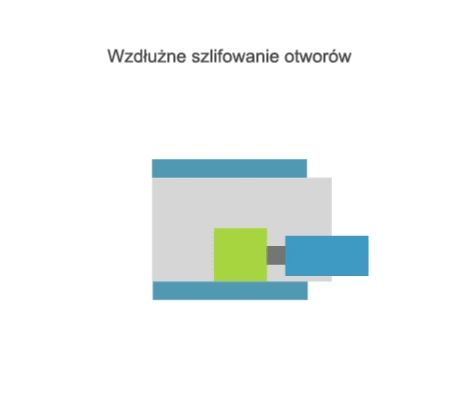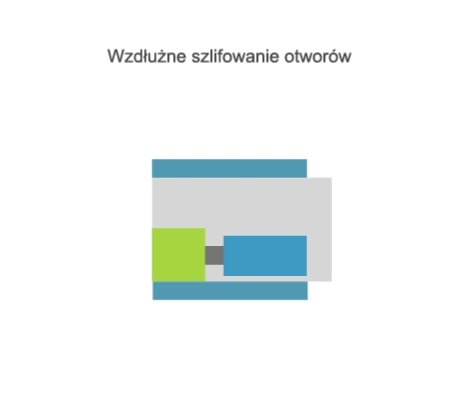
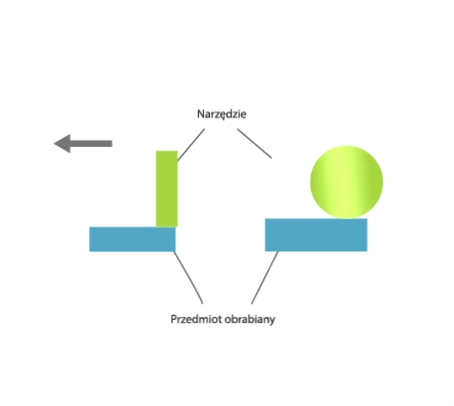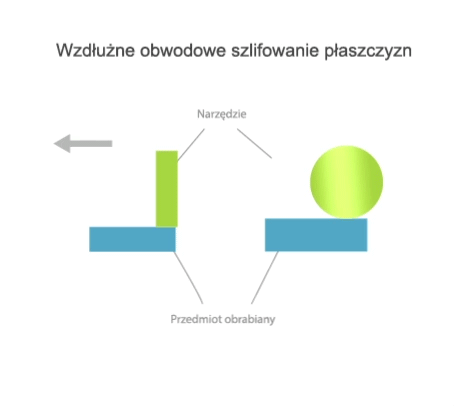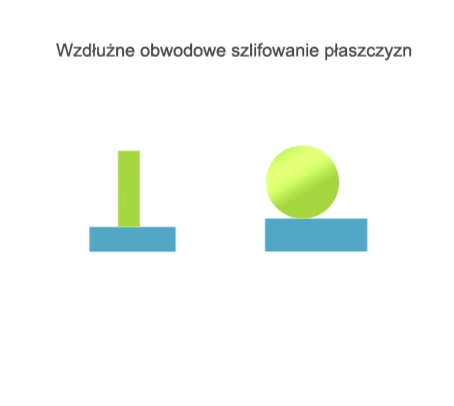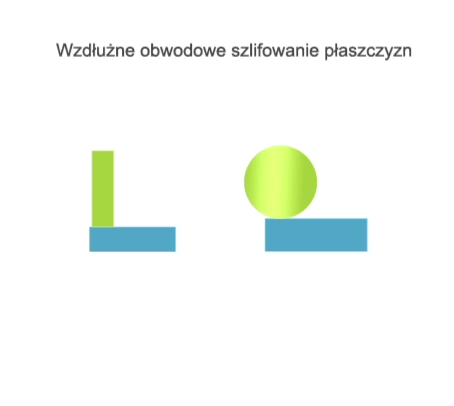
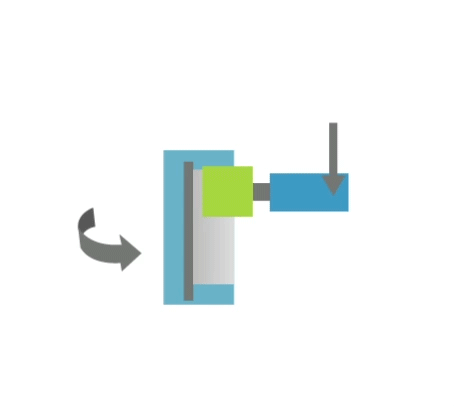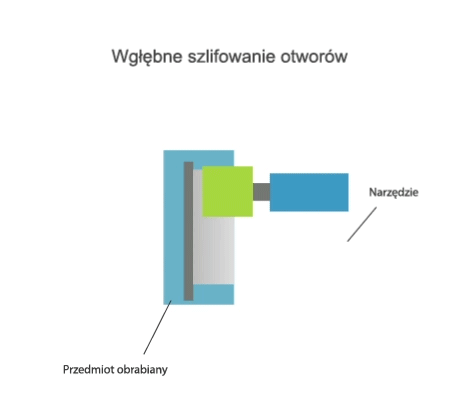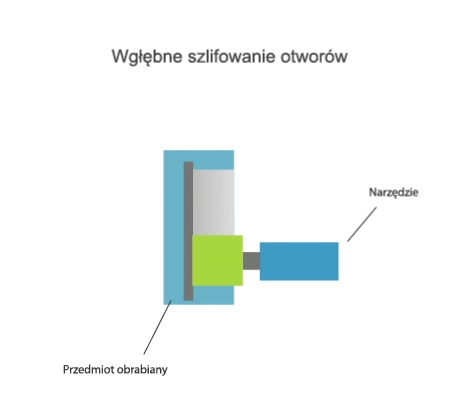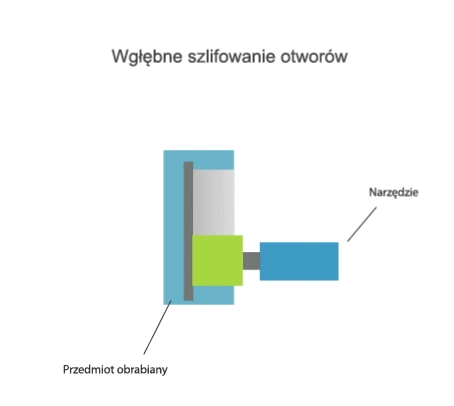
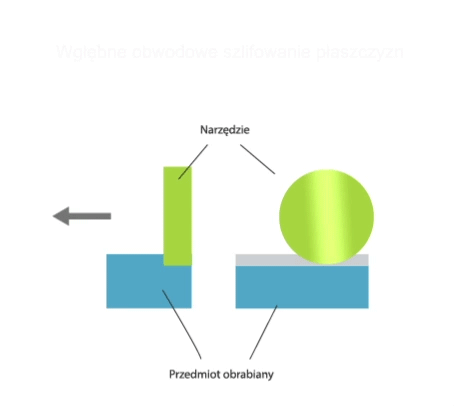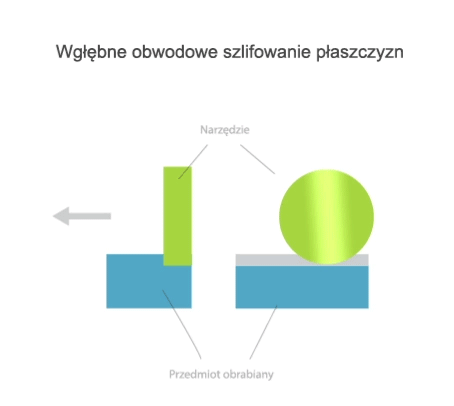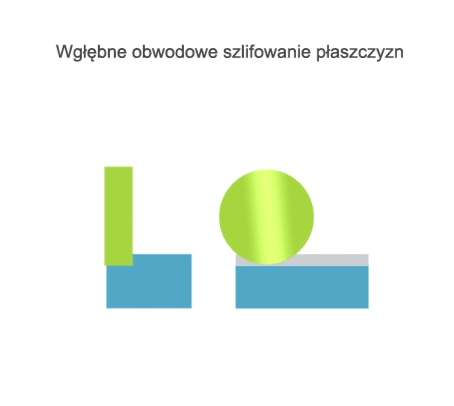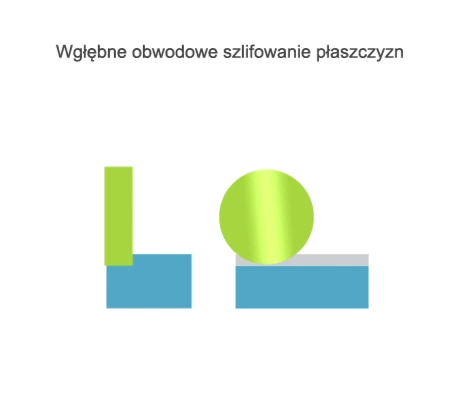
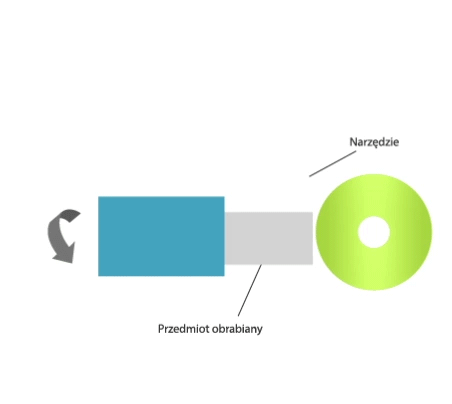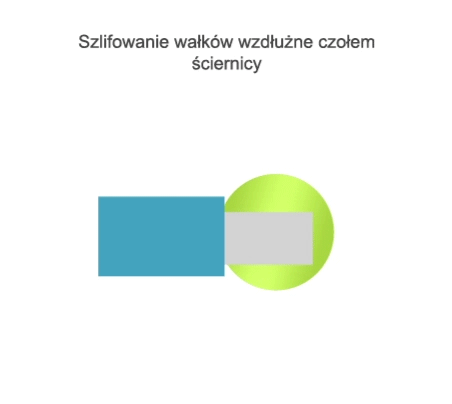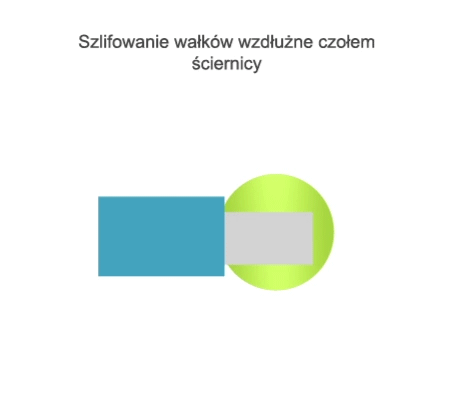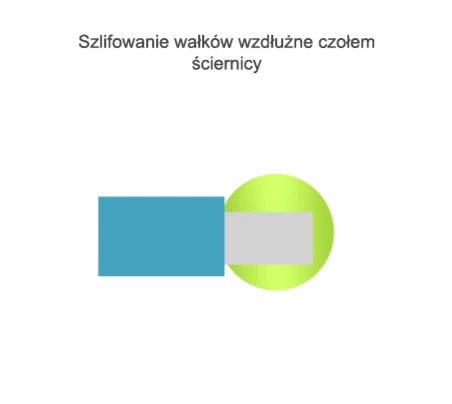
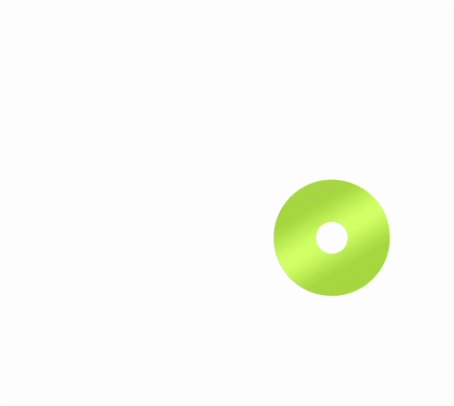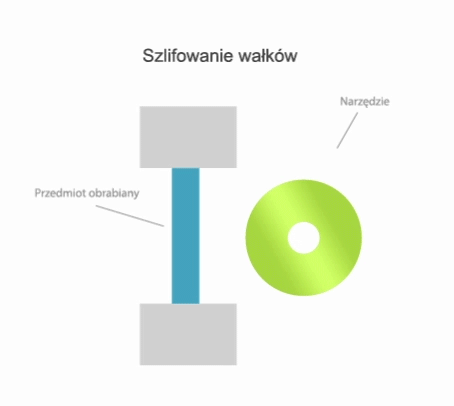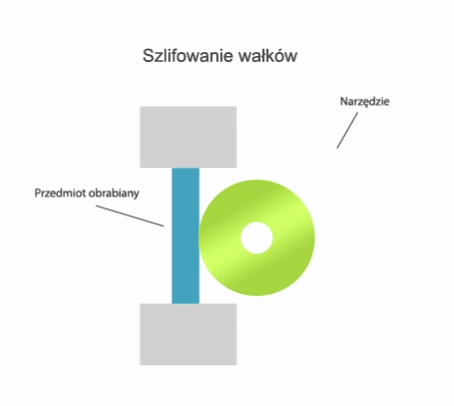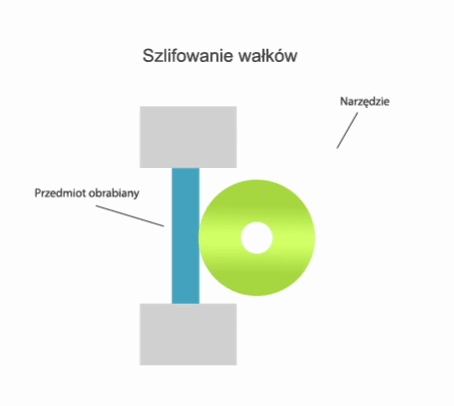
Grinding is a method of machining in which a cutting tool called a grinding wheel (or abrasive belt) performs the primary motion (usually rotary motion), while the auxiliary motion may be performed by the workpiece alone, by the grinding wheel alone, or by the grinding wheel and the workpiece.
With regard to the shape of the machined surfaces, a distinction is made between:
- grinding of external and internal rotating surfaces,
- grinding of non-rotating surfaces (flat or curved).
In the field of rotary grinding, a distinction is made between the method of clamping and driving the workpiece:
- centre-type grinding – where the workpiece is clamped in a headstock and tailstock or grinding chuck and the rotary motion drive is transmitted by a carrier,
- centreless grinding – where the workpiece rests on or moves along a guide rail and an auxiliary rotary or progressive motion is imparted by a disc wheel (on the opposite side, the workpiece remains in contact with the grinding wheel).