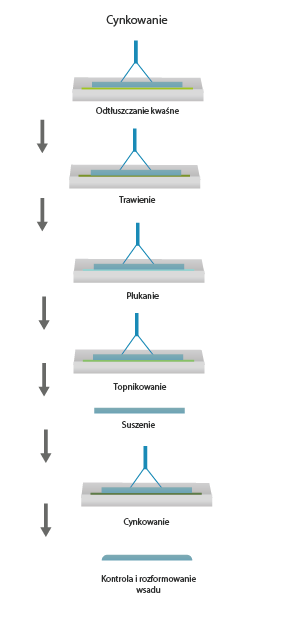
Galvanisation is the thermochemical process of coating the surface of steel objects with a layer of zinc. It prevents corrosion. It consists in the creation of a protective anodic layer on the surface of the steel object.

Galvanisation
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
improving the corrosion resistance of steel surfaces
Use in industry
metallurgy, automotive, aircraft, construction industries
Alternative technologies
- painting
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- protects metal from corrosion
- increases component life
- resistance to acidic substances
Disadvantages
- can be removed with a magnet
- the galvanised coating is prone to chipping and creating an uneven surface
- galvanised surfaces are very hard and durable making them unsuitable for applications where flexibility is required
- unweldable zinc coating
Workpiece material types
- steel
- cast iron
Examples of products
- pipes
- steel structures
- tanks
- steel sheets
- steel tapes
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- galvanising line
Required competences
- none
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none