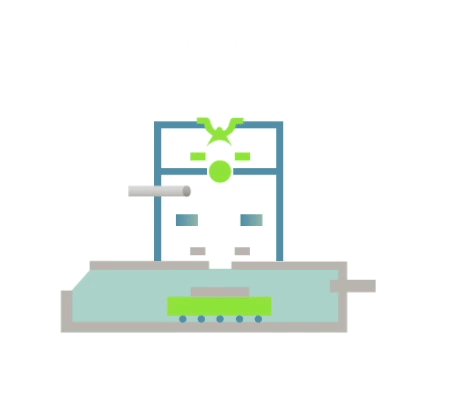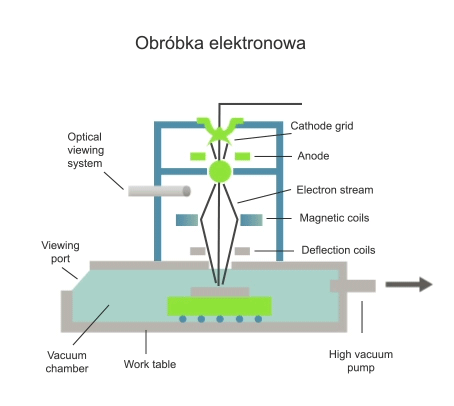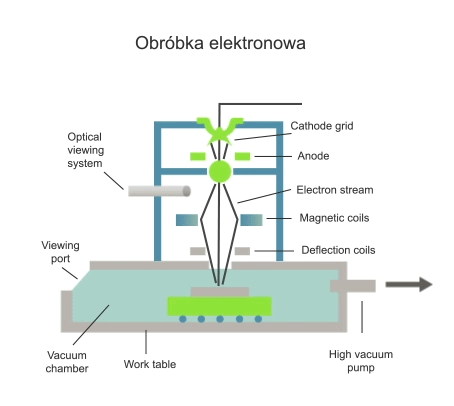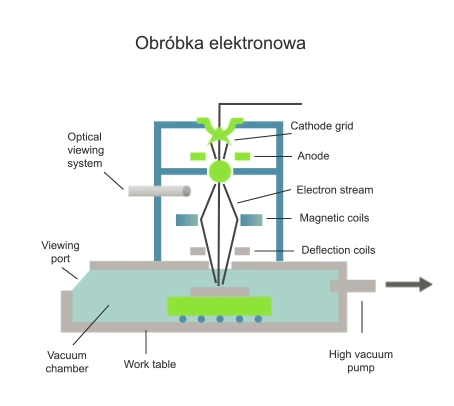
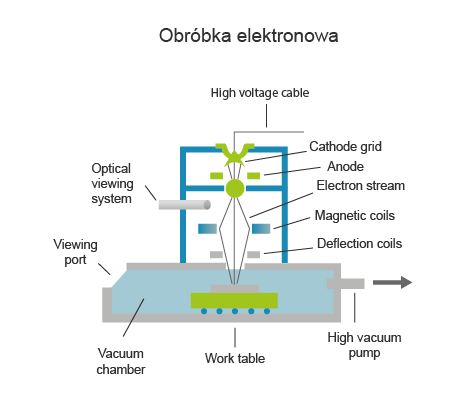
Electron beam machining is a machining process that uses the vapourisation of workpiece material by a stream of electrons emitted from a suitably heated electrode-cathode under vacuum conditions. In the case of welding, the contact area of the workpieces to be joined is molten by the heat generated by bombarding them in a vacuum with a concentrated beam of high-energy electrons.

Electron beam machining
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
high-precision machining of very difficult-to-machine materials (e.g. stainless steels, nickel and cobalt alloys, titanium alloys) in various shapes, subtractive manufacturing of holes, cut-outs and profiles, possibility of machining miniature components, welding of components
Use in industry
aviation industry, automotive industry, mould and die production, precision mechanics
Alternative technologies
- laser beam machining
- plasma arc machining
- micromachining
- bonding/welding
- welding
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- possibility of more efficient machining of hard and brittle materials (compared to conventional machining)
- possibility of machining small holes with high dimensional accuracy (compared to conventional machining)
- little change in the mechanical properties and structure of the machined material (compared to plasma arc machining)
- possibility of obtaining low surface roughness and high dimensional accuracy of the machined parts (compared to conventional machining and plasma arc machining)
- welding process is performed without the use of a binder
Disadvantages
- relatively high investment and tooling costs
- need for highly skilled operators to operate the machining station
- inability to machine large workpieces
- relatively low volumetric efficiency of material removal (compared to alternative techniques)
- high power consumption
Workpiece material types
- stainless steel
- nickel alloys
- cobalt alloys
- titanium alloys
Examples of products
- aircraft engine components
- turbine blades
- specialized details for flight control systems
- details for the production of aircraft seats
- details for the production of shock absorbers
- brake booster components
- components for advanced measuring instruments
- injection mold details for the production of plastic components
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- electron beam machine
- tooling
- vacuum pump
Required competences
- training in erosion machining and abrasive blasting
- training in CNC machine programming
- extensive practical experience in subtractive manufacturing
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- Warsaw University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none