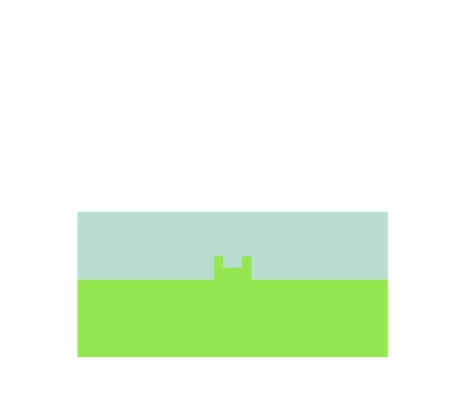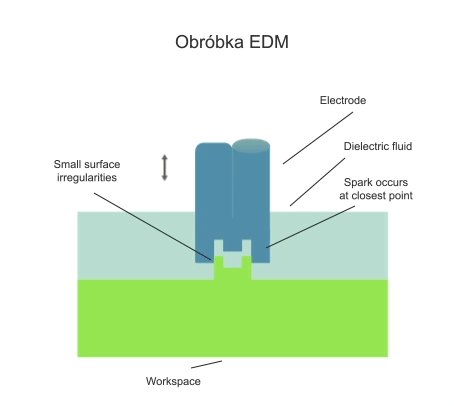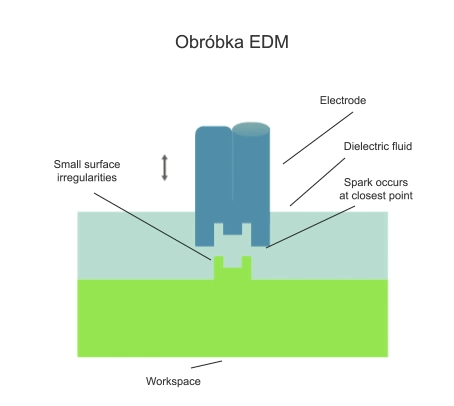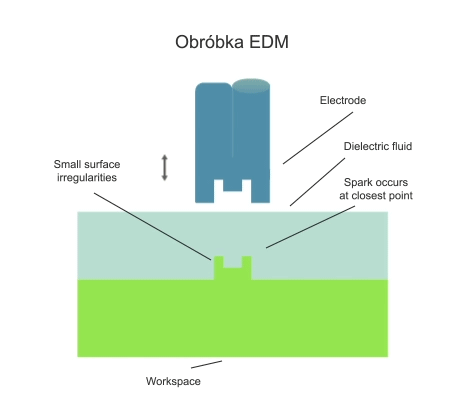
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a subtractive manufacturing process in which a layer of workpiece material is removed by the action of a series of electrical discharges in the gap between the working electrode and the workpiece. The discharges are initiated by a voltage of several tens of volts and always take place in a dielectric fluid.
Electrical discharge machining can be divided into:
- electrical discharge sawing (EDS) – which involves the removal of particles from the outer layers of the electrode materials by electrical erosion induced by non-stationary electrical discharges;
- electric discharge impulse (EDI) – which involves the induction of electrical erosion by stationary electrical discharges.