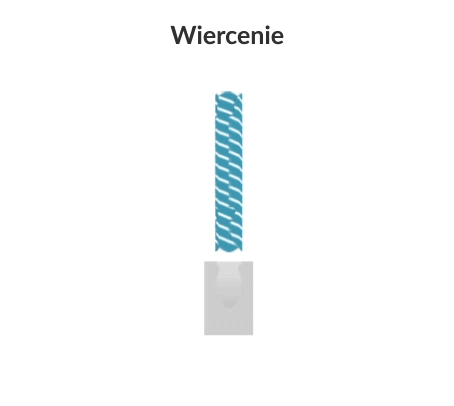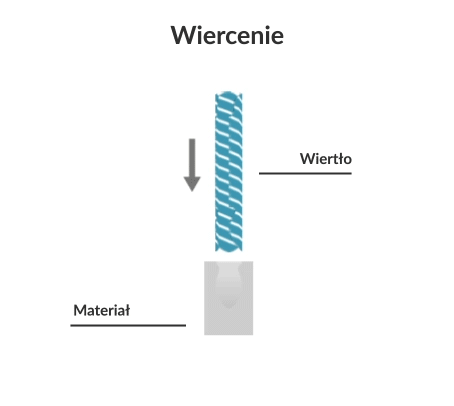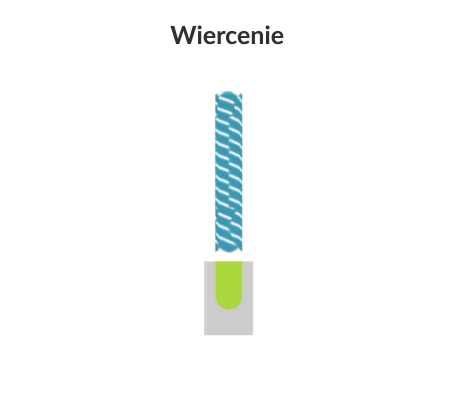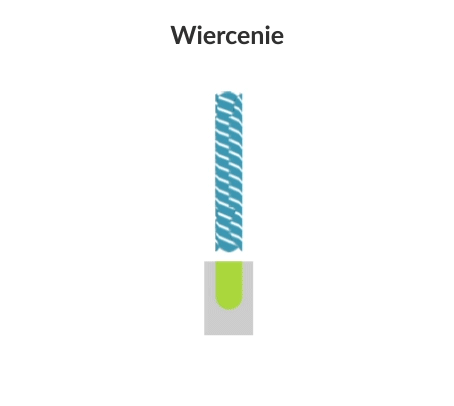
Drilling is a machining process that involves the subtractive manufacturing of cylindrical holes in solid material using single- or multi-blade cutting tools known as drills. During drilling, the primary (rotary) motion is performed by the tool or workpiece (lathe drilling). The feed motion is performed by the tool or the workpiece in a direction parallel to the drill axis.

Drilling
pl.
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
batch, unit
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
subtractive manufacturing (usually roughing) of holes in a solid piece of material
Industry usage
all industries
Alternative technologies
- MQCL drilling
- cryogenic drilling
- boring
- hole milling
- broaching
- laser beam machining
- plasma arc machining
- EDM machining
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- versatile technique for the subtractive manufacturing of holes
Disadvantages
- use of machining fluids that are not inert to people and the environment
- significant tooling and fixture costs
- possibility of significant electricity costs (roughing)
- moderate quality of machined surfaces
Workpiece material types
- all material groups
- ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals
- non-ferrous metals alloys
- hard materials
- hardened materials
Examples of products
- holes in metal structural components e.g. steel beams
- components for furniture production (e.g. fittings; handles; fasteners)
- components for hydraulic and pneumatic systems
- parts for the automotive industry (e.g. brake discs; gearboxes; suspension components)
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- drilling machine
- milling machine or lathe
- cutting tools
- tooling
- machining fluids (optional)
Required competences
- training in machining
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- West Pomeranian University of Technology
- University of Zielona Góra
- Poznan University of Technology
- Opole University of Technology
- Wrocław University of Science and Technology
Legal conditions
- none