Chrome plating is achieved by the process of electroplating, a technique in which dissolved metal cations are reduced in a salt electrolyte bath to form a seamless metal coating on the desired object. Dirt is first removed from the workpiece, and often a layer of material is pre-treated before being placed in the chrome bath.

Chrome plating
Type of technology
Development phase
Level of innovation
Scale of production
mass
Technology readiness level TRL
Description of the technology
Purpose of use
improving corrosion resistance, increasing hardness or enhancing appearance
Use in industry
automotive industry, mechanical industry
Alternative technologies
- none
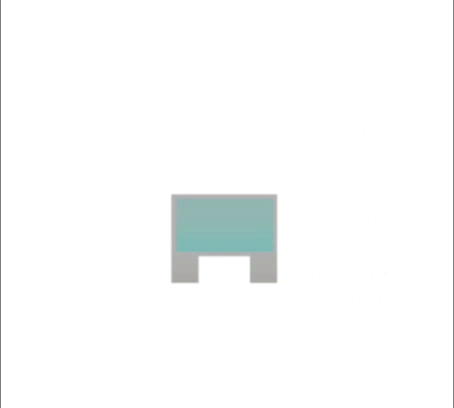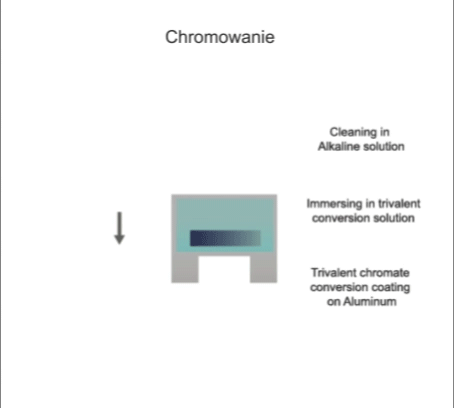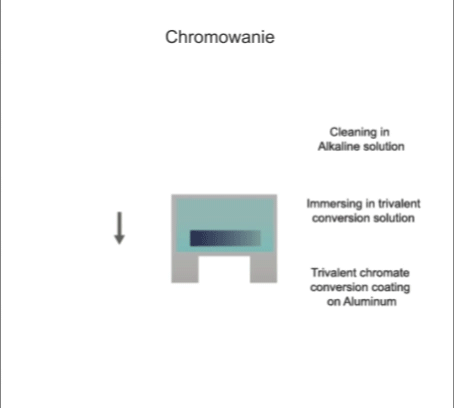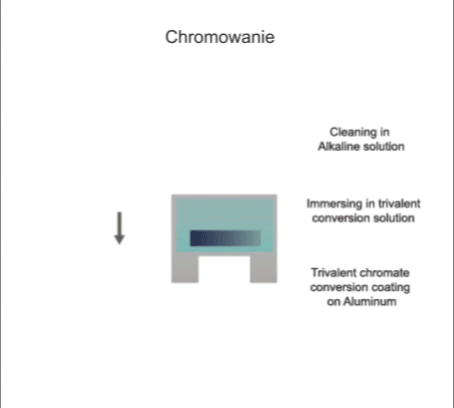
Visualisation of action
Advantages
- high corrosion resistance
- high mechanical resistance of the surface
- high hardness
- high abrasion resistance
- high aesthetic qualities
Disadvantages
- high toxicity
Workpiece material types
- steel
Examples of products
- fasteners
- automotive details (rims/bumpers/side moldings and vehicle interior components)
- bicycle components (handlebars/forks/rims/equipment)
- speaker housings
- knobs
- audio/video equipment details
- industrial machinery and equipment components (covers/knobs and control panels)
- architectural details (handrails/balustrades and other decorative building elements)
Implementation of the technology
Required resources
- chrome plating bath
Required competences
- knowledge of materials science
Environmental aspects
Expert evaluation
Development centers
- AGH University of Krakow
- Opole University of Technology
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science of Polish Academy of Sciences
- Warsaw University of Technology
- Cracow University of Technology
Legal conditions
- none