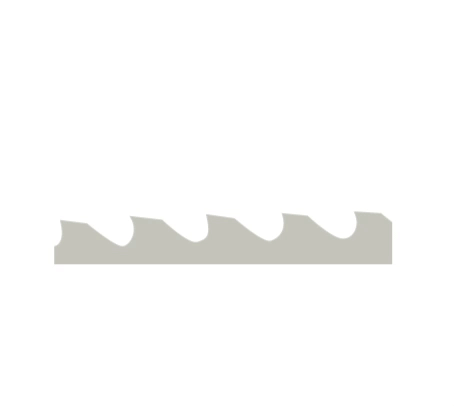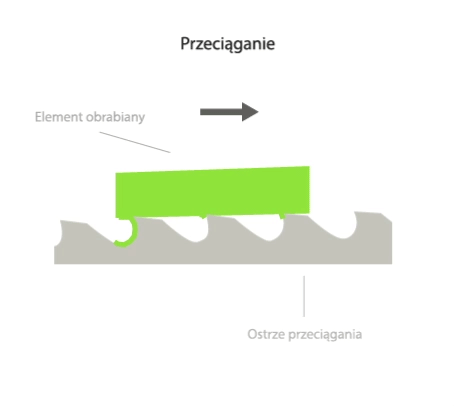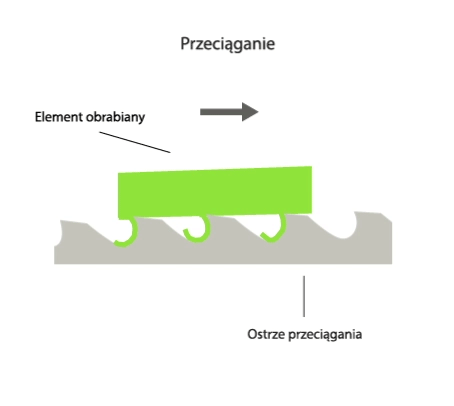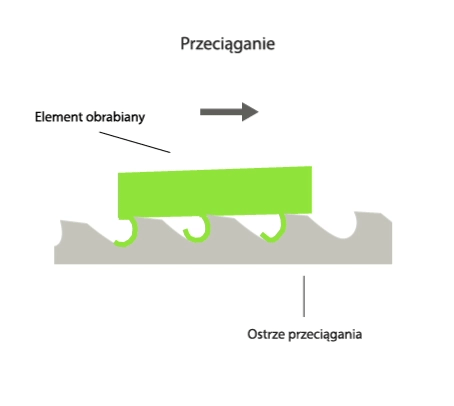
Broaching is a method of machining in which the entire machining allowance is removed in a single pass with a multi-blade tool called a broach.
In broaching, the shape of the machined part is directly determined by the shape of the tool in the cross section. During broaching, the workpiece is stationary while the broach performs a rectilinear primary motion. In the working part of the tool, there are cutting edges of different heights or widths, so that successive layers of workpiece material are cut by successive cutting edges during the working motion of the tool.