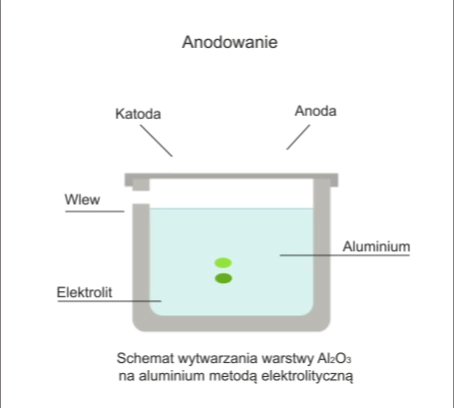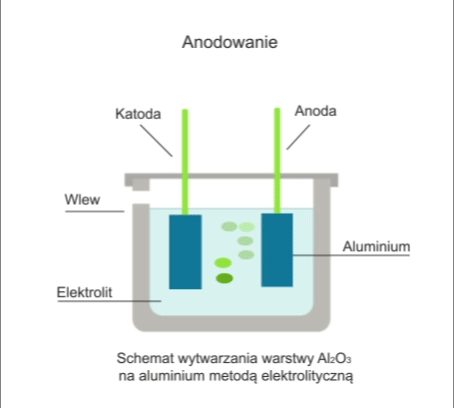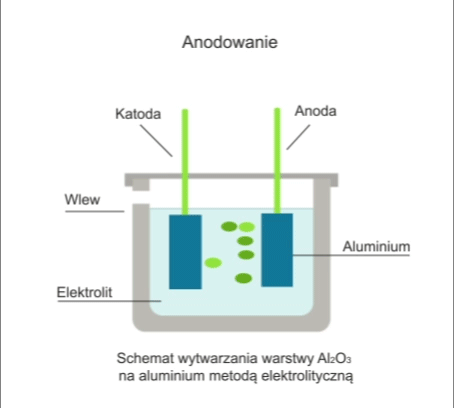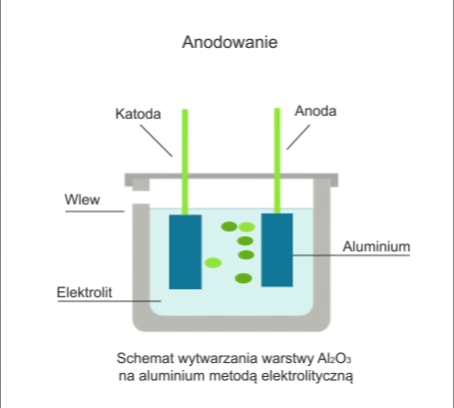
The process involves the electrolytic formation of an oxide layer on the workpiece.
The workpiece is immersed in an electrolytic bath in which it acts as an anode. In anodising, the electrolyte is usually sulphuric acid. During electrolysis, when a DC voltage of 12-20V is applied to the electrodes, oxygen is released, which reacts with the metal to form a transparent oxide film.