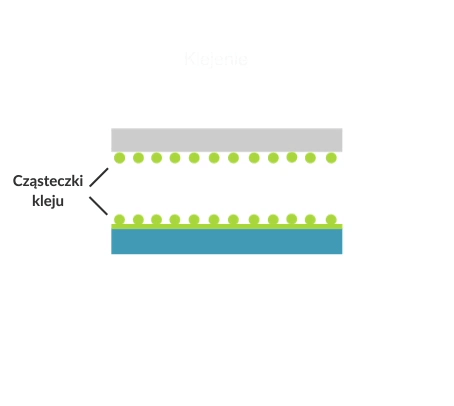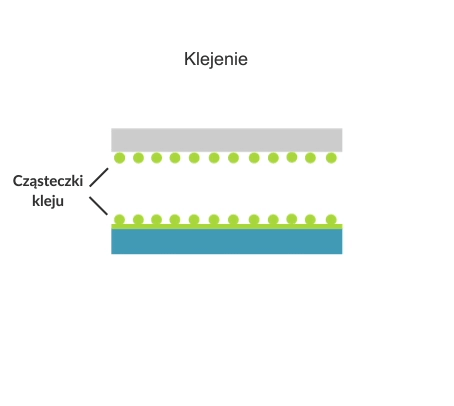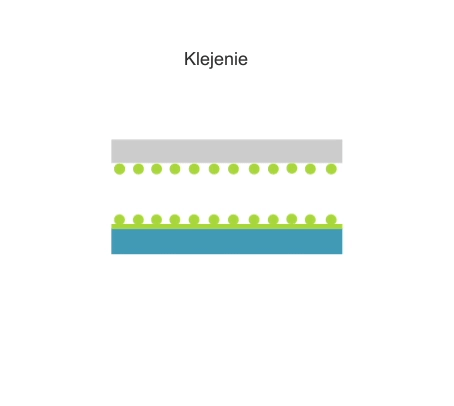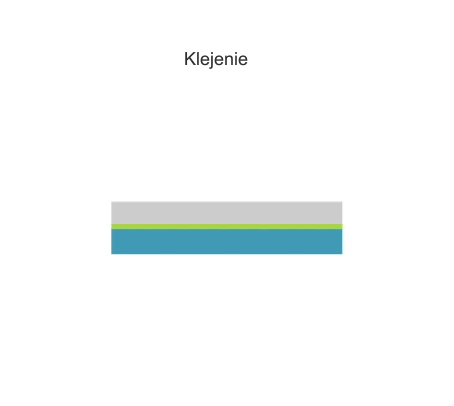
Adhesive bonding is the permanent joining of two or more parts by the adhesive and the cohesive action of the adhesive on the parts being joined.
There are two main steps in the adhesive bonding process: the application of the adhesive and the joining of the parts. In industrial applications, adhesive points or lines often need to be placed in precise locations on or inside the assembly.
When bonding metals, an adhesive with a low surface tension should be chosen, as the lower the viscosity of the adhesive, the easier it is to wet the surface of the object being bonded. Most metal adhesives are two-part adhesives consisting of a base and a hardener. Acrylic and epoxy adhesives are the most commonly used.