Accumulative roll bonding (ARB) is an experimental rolling process using the effect of severe plastic deformation (SPD), which is not yet used as an industrial process for metalworking. It aims to refine the crystalline structure of the metal alloys concerned, thereby increasing their yield strength.
It is well known that the stress in polycrystalline metal flow is directly related to grain size or, more generally, to any microstructural feature that describes the average distance between structural defects (grain boundaries, high-angle cell boundaries). Compared to other standard rolling processes, ARB allows a higher degree of deformation.
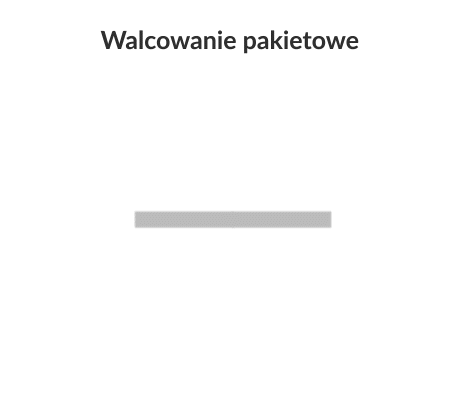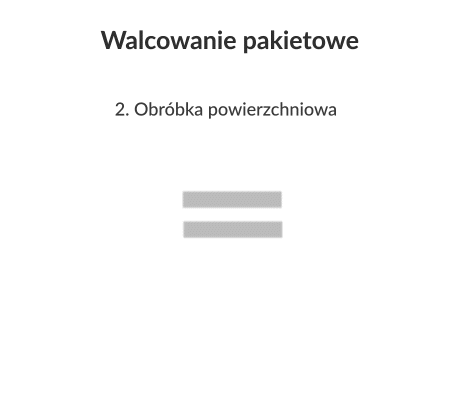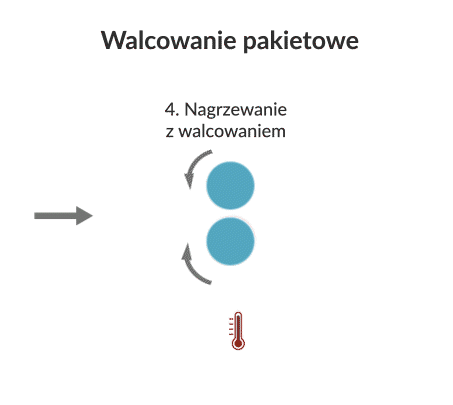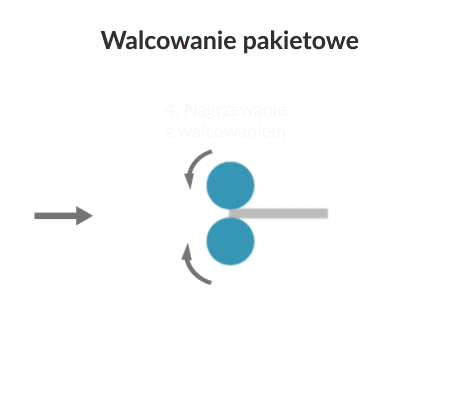
The process consists of rolling two overlapping sheets after heating them to a suitable temperature to a predetermined degree of thickness reduction (e.g. 50%). Under appropriate ARB conditions (i.e. rolling temperature and speed), a bonding layer is formed between the sheets during the deformation process, due to both the temperature and the effect of strong plastic deformation. The product of the first rolling cycle is cut into two similar sheets, which are overlapped and re-rolled in the same way as the first cycle.